Clinical features and genetic analysis of childhood sitosterolemia: Two case reports and literature review
- PMID: 30985648
- PMCID: PMC6485811
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015013
Clinical features and genetic analysis of childhood sitosterolemia: Two case reports and literature review
Abstract
Rationale: Sitosterolemia is a rare autosomal recessive disorder of dyslipidemia due to mutations of genes ABCG5 and ABCG8, leading to highly elevated plasma levels of plant sterols and expanded body pools of cholesterol.
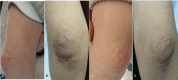
Patient concerns: We present a 9-year-old and a 7-year-old Chinese boy with hypercholesterolemia and xanthomas of sitosterolemia due to ABCG5 gene mutations. We also make a literature review of another 30 sitosterolemic children cases that have been reported with virulence ABCG5 gene mutations.
Diagnosis: We took peripheral blood samples from 2 patients and their parents to conduct genetic analysis by next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies.
Interventions: The 2 patients received dietary modifications without pharmaceuticals treatment.
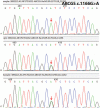
Outcomes: A c.1166G>A (Arg389His) homozygosis mutation in exon 9 was observed in case 1, whereas a c.751C>T (Gln251*) homozygosis mutation in exon 6 was found in case 2. Literature review found another 30 pediatric cases with sitosterolemia due to ABCG5 gene mutation. The lipid profile was normalized and xanthomas got smaller with combined therapy of a combined low-cholesterol and low-phytosterols diet.
Lessons: These suggested that in patients (especially Asian patients) with multiple xanthomas, severe hypercholesterolemia, or elevated low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol, sitosterolemia should be considered in the differential diagnosis. Early diagnosis is important, and restriction of both cholesterol and phytosterols diet should suggested for these patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Tzavella E, Hatzimichael E, Kostara C, et al. Sitosterolemia: a multifaceted metabolic disorder with important clinical consequences. J Clin Lipidol 2017;11:1095–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

