Regulation of signaling mediated by nucleic acid sensors for innate interferon-mediated responses during viral infection
- PMID: 30985869
- PMCID: PMC7110195
- DOI: 10.1093/intimm/dxz034
Regulation of signaling mediated by nucleic acid sensors for innate interferon-mediated responses during viral infection
Abstract
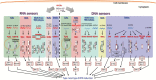
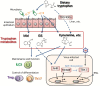
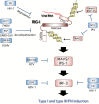
Type I and type III interferons are important anti-viral cytokines that are massively induced during viral infection. This dynamic process is regulated by many executors and regulators for efficient eradication of invading viruses and protection from harmful, excessive responses. An array of innate sensors recognizes virus-derived nucleic acids to activate their downstream signaling to evoke cytokine responses including interferons. In particular, a cytoplasmic RNA sensor RIG-I (retinoic acid-inducible gene I) is involved in the detection of multiple types of not only RNA viruses but also DNA viruses. Accumulating findings have revealed that activation of nucleic acid sensors and the related signaling mediators is regulated on the basis of post-translational modification such as ubiquitination, phosphorylation and ADP-ribosylation. In addition, long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been implicated as a new class of regulators in innate signaling. A comprehensive understanding of the regulatory mechanisms of innate sensor activation and its signaling in host-virus interaction will provide a better therapeutic strategy to efficiently control viral infection and maintain immune homeostasis.
Keywords: RIG-I; interferon; pattern-recognition receptors; signal transduction; virus infection.
© The Japanese Society for Immunology. 2019. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
-
- Nagano Y. and Kojima Y. 1954. [Immunizing property of vaccinia virus inactivated by ultraviolets rays]. C. R. Seances Soc. Biol. Fil. 148:1700. - PubMed
-
- Isaacs A. and Lindenmann J. 1957. Virus interference. I. The interferon. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 147:258. - PubMed
-
- Kumar H., Kawai T. and Akira S. 2011. Pathogen recognition by the innate immune system. Int. Rev. Immunol. 30:16. - PubMed
-
- Alexopoulou L., Holt A. C., Medzhitov R. and Flavell R. A. 2001. Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptor 3. Nature 413:732. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

