PD-L1 Expression in Systemic Immune Cell Populations as a Potential Predictive Biomarker of Responses to PD-L1/PD-1 Blockade Therapy in Lung Cancer
- PMID: 30986912
- PMCID: PMC6479779
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20071631
PD-L1 Expression in Systemic Immune Cell Populations as a Potential Predictive Biomarker of Responses to PD-L1/PD-1 Blockade Therapy in Lung Cancer
Abstract
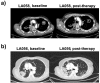
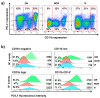
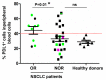
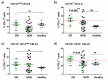
PD-L1 tumor expression is a widely used biomarker for patient stratification in PD-L1/PD-1 blockade anticancer therapies, particularly for lung cancer. However, the reliability of this marker is still under debate. Moreover, PD-L1 is widely expressed by many immune cell types, and little is known on the relevance of systemic PD-L1⁺ cells for responses to immune checkpoint blockade. We present two clinical cases of patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and PD-L1-negative tumors treated with atezolizumab that showed either objective responses or progression. These patients showed major differences in the distribution of PD-L1 expression within systemic immune cells. Based on these results, an exploratory study was carried out with 32 cases of NSCLC patients undergoing PD-L1/PD-1 blockade therapies, to compare PD-L1 expression profiles and their relationships with clinical outcomes. Significant differences in the percentage of PD-L1⁺ CD11b⁺ myeloid cell populations were found between objective responders and non-responders. Patients with percentages of PD-L1⁺ CD11b⁺ cells above 30% before the start of immunotherapy showed response rates of 50%, and 70% when combined with memory CD4 T cell profiling. These findings indicate that quantification of systemic PD-L1⁺ myeloid cell subsets could provide a simple biomarker for patient stratification, even if biopsies are scored as PD-L1 null.
Keywords: PD-L1; biomarker; immune checkpoint blockade; immunotherapy; lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gato-Canas M., Zuazo M., Arasanz H., Ibanez-Vea M., Lorenzo L., Fernandez-Hinojal G., Vera R., Smerdou C., Martisova E., Arozarena I., et al. PDL1 Signals through Conserved Sequence Motifs to Overcome Interferon-Mediated Cytotoxicity. Cell Rep. 2017;20:1818–1829. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.07.075. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Herbst R.S., Baas P., Kim D.W., Felip E., Perez-Gracia J.L., Han J.Y., Molina J., Kim J.H., Arvis C.D., Ahn M.J., et al. Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2016;387:1540–1550. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01281-7. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

