Smart Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Protein Delivery
- PMID: 30986952
- PMCID: PMC6523670
- DOI: 10.3390/nano9040511
Smart Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Protein Delivery
Abstract
Mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSN) have attracted a lot of attention during the past decade which is attributable to their versatile and high loading capacity, easy surface functionalization, excellent biocompatibility, and great physicochemical and thermal stability. In this review, we discuss the factors affecting the loading of protein into MSN and general strategies for targeted delivery and controlled release of proteins with MSN. Additionally, we also give an outlook for the remaining challenges in the clinical translation of protein-loaded MSNs.
Keywords: controlled release; mesoporous silica nanoparticle; protein delivery; stimulus responsive MSN.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
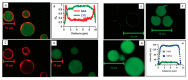



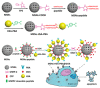

References
-
- Goeddel D.V., Kleid D.G., Bolivar F., Heyneker H.L., Yansura D.G., Crea R., Hirose T., Kraszewski A., Itakura K., Riggs A.D. Expression in Escherichia coli of chemically synthesized genes for human insulin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1979;76:106–110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.106. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

