Morphology and Structure of Electrodeposited Prussian Blue and Prussian White Thin Films
- PMID: 30987083
- PMCID: PMC6480295
- DOI: 10.3390/ma12071103
Morphology and Structure of Electrodeposited Prussian Blue and Prussian White Thin Films
Abstract
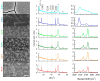
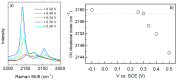
The compound Prussian Blue (PB), and its reduced form Prussian White (PW) are nowadays considered, in applied and fundamental research groups, as potential materials for sustainable energy storage devices. In this work, these compounds were prepared by potentiostatic electrochemical synthesis, by using different deposition voltages and thicknesses. Thick, compact and uniform layers were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and Raman spectroscopy. Results have shown a well-defined transition voltage for growing Prussian Blue phases and a strong dependence of the morphology/growing orientation of the samples as a function of applied potential and thickness. For the negative potential tested of -0.10 V vs. SCE, a mixture of cubic and rhombohedral phases was observed.
Keywords: Electrodeposition; Hexacyanoferrate; Prussian Blue; Prussian White.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Keggin J.F., Miles F.D. Structures and Formulae of the Prussian Blues and Related Compounds. Nature. 1936;137:577. doi: 10.1038/137577a0. - DOI
-
- Davidson D., Welo L.A. The Nature of Prussian Blue. J. Phys. Chem. 1928;32:1191–1196. doi: 10.1021/j150290a007. - DOI
-
- Kraft A. Electrochromism: A fascinating branch of electrochemistry. ChemTexts. 2018;5 doi: 10.1007/s40828-018-0076-x. - DOI
-
- Amarnath C.A., Sawant S.N. Tailoring synthesis strategies for polyaniline-prussian blue composite in view of energy storage and H2O2 sensing application. Electrochim. Acta. 2019;295:294–301. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2018.10.132. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

