Photocatalytic Activity of TiO₂ Nanofibers: The Surface Crystalline Phase Matters
- PMID: 30987165
- PMCID: PMC6523154
- DOI: 10.3390/nano9040535
Photocatalytic Activity of TiO₂ Nanofibers: The Surface Crystalline Phase Matters
Abstract
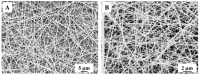
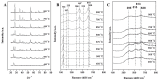
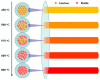
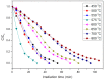
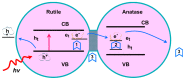
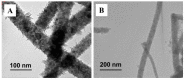
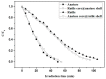
The crystal phases and surface states of TiO₂ can intrinsically determine its performance in the applications of photocatalysis. Here, we prepared TiO₂ nanofibers with different crystal phase contents by electrospinning followed via calcination at different temperatures. The TiO₂ nanofibers were characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Raman spectrometry, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and photocatalytic performance testing. The results showed that the phases of TiO₂ nanofibers were layered, that surface crystal phase transition rate was faster than that of internal layers contributed the difference in the ratio of anatase and rutile in the outer and inner layer of TiO₂ nanofibers. The TiO₂ nanofibers obtained at 575 °C had the best photocatalytic activity, taking only 25 min to degrade Rhodamine B. At 575 °C, the rutile content of the sample surface was about 80 wt.%, while the internal rutile content was only about 40 wt.%. Subsequently, we prepared two different structures of anatase-rutile core-shell TiO₂ nanofibers. The core-shell structure can be clearly seen by TEM characterization. The photocatalytic activity of two kinds of core-shell TiO₂ nanofibers was tested. The results showed that the photocatalytic activity was close to that of the pure phase TiO₂ nanofibers, which corresponded with the surface phase. This further proves that the photocatalytic activity of the material is mainly affected by its surface structure.
Keywords: TiO2 nanofibers; core-shell structure; crystal phase transition; mixed phases; photocatalytic activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Nasikhudin, Ismaya E.P., Diantoro M., Kusumaatmaja A., Triyana K. Preparation of PVA/TiO2 composites nanofibers by using electrospinning method for photocatalytic degradation. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017;202:012011. doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/202/1/012011. - DOI
-
- Compagnoni M., Ramis G., Freyria F.S., Armandi M., Bonelli B., Rossetti I. Photocatalytic processes for the abatement of N-containing pollutants from waste water. part 1: Inorganic pollutants. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017;17:3632–3653. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2017.14006. - DOI
-
- Zhang L., Wang L., Wei Y., Zhang M., Jiang H., Li J., Li S., Li J. Electrospun TiO2 nanofibers surface-loaded with Ag nanoparticles as a sensitizer and their enhanced effect in photocatalytic applications. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2015;2015:5039–5044. doi: 10.1002/ejic.201500609. - DOI
-
- Etacheri V., Valentin C.D., Schneider J., Bahnemann D., Pillai S.C. Visible-light activation of TiO2 photocatalysts: Advances in theory and experiments. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2015;25:1–29. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotochemrev.2015.08.003. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

