A Study of 5-Fluorouracil Desorption from Mesoporous Silica by RP-UHPLC
- PMID: 30987237
- PMCID: PMC6479690
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24071317
A Study of 5-Fluorouracil Desorption from Mesoporous Silica by RP-UHPLC
Abstract
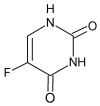
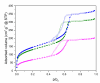
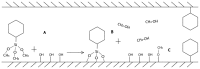
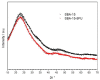
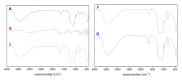
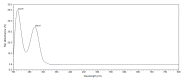
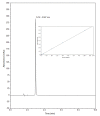
In cancer treatment, the safe delivery of the drug to the target tissue is an important task. 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), the well-known anticancer drug, was encapsulated into the pores of unmodified mesoporous silica SBA-15, as well as silica modified with 3-aminopropyl and cyclohexyl groups. The drug release studies were performed in two different media, in a simulated gastric fluid (pH = 2) and in a simulated body fluid (pH = 7) by RP-UHPLC. The simple and rapid RP-UHPLC method for quantitative determination of 5-fluorouracil released from unmodified and modified mesoporous silica SBA-15 was established on ODS Hypersil C18 column (150 × 4.6 mm, 5 µm) eluted with mobile phase consisted of methanol: phosphate buffer in volume ratio of 3:97 (v/v). Separation was achieved by isocratic elution. The flow rate was kept at 1 mL/min, the injection volume was set at 20 µL and the column oven temperature was maintained at 25 °C. The effluent was monitored at 268 nm. This paper provides information about the quantitative determination of the released 5-FU from silica. It was found out that larger amount of the drug was released in neutral pH in comparison with the acidic medium. In addition, surface functionalisation of silica SBA-15 influences the release properties of the drug.
Keywords: 5-fluorouracil; RP-UHPLC; desorption; mesoporous silica.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



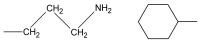

References
-
- Böttcher H., Slowik P., Süβ W. Sol-Gel Carrier Systems for Controlled Drug Delivery. J. Sol–Gel Sci. Technol. 1998;13:277. doi: 10.1023/A:1008603622543. - DOI
-
- Manzano M., Vallet-Regí M. New developments in ordered mesoporous materials for drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. 2010;20:5593–5604. doi: 10.1039/b922651f. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

