MicroRNA-7a ameliorates neuropathic pain in a rat model of spinal nerve ligation via the neurofilament light polypeptide-dependent signal transducer and activator of transcription signaling pathway
- PMID: 30987515
- PMCID: PMC6537231
- DOI: 10.1177/1744806919842464
MicroRNA-7a ameliorates neuropathic pain in a rat model of spinal nerve ligation via the neurofilament light polypeptide-dependent signal transducer and activator of transcription signaling pathway
Abstract
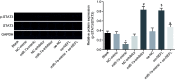
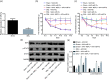
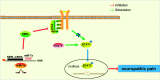
Neuropathic pain is a type of chronic pain induced by either central or peripheral nerve injury. MicroRNAs have been recently linked to many diseases, including neuropathic pain. However, the role of miR-7a in neuropathic pain still remains elusive. Thus, we aim to investigate the effects of miR-7a on neuropathic pain based on the spinal nerve ligation rat model. After establishment of spinal nerve ligation rat models, rats were infected with adeno-associated virus-neurofilament light polypeptide, adeno-associated virus-miR-7a or treated with metformin. The paw withdrawal threshold and paw withdrawal latency were assessed afterward, and the expression of miR-7a and neurofilament light polypeptide as well as their interaction was determined. Subsequently, miR-7a was overexpressed or silenced in dorsal root ganglion cells to investigate the role of miR-7a in neuropathic pain. Furthermore, the regulatory effect of neurofilament light polypeptide on neuropathic pain was detected using plasmid overexpressing neurofilament light polypeptide. Spinal nerve ligation rat model exhibited upregulation of neurofilament light polypeptide but downregulation of miR-7a. In addition, neurofilament light polypeptide accumulation or miR-7a inhibition decreased paw withdrawal threshold and paw withdrawal latency. Then, neurofilament light polypeptide accumulation or miR-7a inhibition was observed to increase the phosphorylation level of signal transducer and activator of transcription. miR-7a was found to directly target neurofilament light polypeptide and downregulate neurofilament light polypeptide. In addition, inhibiting the signal transducer and activator of transcription signaling pathway was also revealed to increase paw withdrawal threshold and paw withdrawal latency. Collectively, our study demonstrated that miR-7a ameliorated neuropathic pain via blocking the signal transducer and activator of transcription signaling pathway by repressing neurofilament light polypeptide. These findings, if taken further, can be of important clinical significance in treating patients with neuropathic pain.
Keywords: Neuropathic pain; microRNA-7a; neurofilament light polypeptide; signal transducer and activator of transcription signaling pathway.
Figures
Similar articles
-
New Vistas in microRNA Regulatory Interactome in Neuropathic Pain.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Feb 25;12:778014. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.778014. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35280258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Down-regulation of microRNA-34c-5p alleviates neuropathic pain via the SIRT1/STAT3 signaling pathway in rat models of chronic constriction injury of sciatic nerve.J Neurochem. 2020 Aug;154(3):301-315. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14998. Epub 2020 Mar 24. J Neurochem. 2020. PMID: 32126145
-
MicroRNA-93 alleviates neuropathic pain through targeting signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.Int Immunopharmacol. 2017 May;46:156-162. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2017.01.027. Epub 2017 Mar 8. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28284149
-
miR-7a alleviates the maintenance of neuropathic pain through regulation of neuronal excitability.Brain. 2013 Sep;136(Pt 9):2738-50. doi: 10.1093/brain/awt191. Epub 2013 Jul 16. Brain. 2013. PMID: 23861446
-
Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Exercise on Neuropathic Pain Induced by Peripheral Nerve Injury in Rat Models.Front Neurol. 2019 Jun 14;10:636. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00636. eCollection 2019. Front Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31258512 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
microRNA-Based Network and Pathway Analysis for Neuropathic Pain in Rodent Models.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Jan 13;8:780730. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.780730. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35096965 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-Based Delivery Systems for Chronic Neuropathic Pain Treatment in Dorsal Root Ganglion.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Jul 18;17(7):930. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17070930. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40733138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Vistas in microRNA Regulatory Interactome in Neuropathic Pain.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Feb 25;12:778014. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.778014. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35280258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitor TPPU Alleviates Nab-Paclitaxel-Induced Peripheral Neuropathic Pain via Suppressing NF-κB Signalling in the Spinal Cord of a Rat.Pain Res Manag. 2023 Feb 8;2023:9058774. doi: 10.1155/2023/9058774. eCollection 2023. Pain Res Manag. 2023. PMID: 36819745 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Micro-RNA for Pain After Surgery: Narrative Review of Animal and Human Studies.Anesth Analg. 2020 Jun;130(6):1638-1652. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000004767. Anesth Analg. 2020. PMID: 32384350 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allegri M, Baron R, Hans G, Correa-Illanes G, Mayoral Rojals V, Mick G, Serpell M. A pharmacological treatment algorithm for localized neuropathic pain. Curr Med Res Opin 2016; 32: 377–384. - PubMed
-
- Jones RC, 3rd, Lawson E, Backonja M. Managing neuropathic pain. Med Clin North Am 2016; 100: 151–167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

