Safety of Dynamic Intravenous Iron Administration Strategies in Hemodialysis Patients
- PMID: 30988164
- PMCID: PMC6500950
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.03970318
Safety of Dynamic Intravenous Iron Administration Strategies in Hemodialysis Patients
Abstract
Background and objectives: Intravenous iron therapy for chronic anemia management is largely driven by dosing protocols that differ in intensity with respect to dosing approach (i.e., dose, frequency, and duration). Little is known about the safety of these protocols.
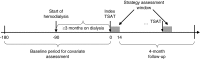
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: Using clinical data from a large United States dialysis provider linked to health care utilization data from Medicare, we constructed a cohort of patients with ESKD aged ≥65 years who initiated and continued center-based hemodialysis for ≥90 days between 2009 and 2012, and initiated at least one of the five common intravenous iron administration strategies; ranked by intensity (the amount of iron given at moderate-to-high iron indices), the order of strategies was 3 (least intensive), 2 (less intensive), 1 (reference), 4 (more intensive), and 5 (most intensive). We estimated the effect of continuous exposure to these strategies on cumulative risks of mortality and infection-related events with dynamic Cox marginal structural models.
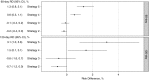
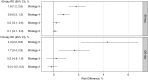
Results: Of 13,249 eligible patients, 1320 (10%) died and 1627 (12%) had one or more infection-related events during the 4-month follow-up. The most and least commonly initiated strategy was strategy 2 and 5, respectively. Compared with the reference strategy 1, more intensive strategies (4 and 5) demonstrated a higher risk of all-cause mortality (e.g., most intensive strategy 5: 60-day risk difference: 1.3%; 95% confidence interval [95% CI], 0.8% to 2.1%; 120-day risk difference: 3.1%; 95% CI, 1.0% to 5.6%). Similarly, higher risks were observed for infection-related morbidity and mortality among more intensive strategies (e.g., strategy 5: 60-day risk difference: 1.8%; 95% CI, 1.2% to 2.6%; 120-day risk difference: 4.3%; 95% CI, 2.2% to 6.8%). Less intensive strategies (2 and 3) demonstrated lower risks of all-cause mortality and infection-related events.
Conclusions: Among dialysis patients surviving 90 days, subsequent intravenous iron administration strategies promoting more intensive iron treatment at moderate-to-high iron indices levels are associated with higher risks of mortality and infection-related events.
Keywords: Administration, Intravenous; Confidence Intervals; Iron; Kidney Failure, Chronic; Medicare; Proportional Hazards Models; anemia; anemia management; comparative safety; dialysis; endstage kidney disease; hemodialysis patients; infections; intravenous iron administration strategies; mortality.
Copyright © 2019 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures

References
-
- KDIGO : KDIGO clinical practice guideline for anemia in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl 2: 279–335, 2012
-
- Kliger AS, Foley RN, Goldfarb DS, Goldstein SL, Johansen K, Singh A, Szczech L: KDOQI US commentary on the 2012 KDIGO clinical practice guideline for anemia in CKD. Am J Kidney Dis 62: 849–859, 2013 - PubMed
-
- Robins JM: The analysis of randomized and nonrandomized AIDS treatment trials using a new approach to causal inference in longitudinal studies. In: Health Service Research Methodology: A Focus on AIDS, edited by Sechrest L, Freeman H, Mulley A, Washington, DC, NCHSR, US Public Health Service, 1989, pp 113–159
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

