Association Between Children's Hospital Visitor Restrictions and Healthcare-Associated Viral Respiratory Infections: A Quasi-Experimental Study
- PMID: 30989226
- PMCID: PMC7107505
- DOI: 10.1093/jpids/piz023
Association Between Children's Hospital Visitor Restrictions and Healthcare-Associated Viral Respiratory Infections: A Quasi-Experimental Study
Abstract
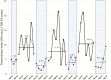
We investigated the effect of annual winter visitor restrictions on hospital respiratory virus transmission. The healthcare-associated (HA) viral respiratory infection (VRI) transmission index (number of HA VRIs per 100 inpatient community-associated VRIs) was 59% lower during the months in which visitor restrictions were implemented. These data prompt consideration for instituting year-round visitor restrictions.
Keywords: enterovirus; healthcare-associated infection; respiratory virus; rhinovirus; visitors.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Journal of the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Pong AL, Beekmann SE, Faltamo MM, et al. . Visitor restriction policies and practices in children’s hospitals in North America: results of an Emerging Infections Network survey. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2018; 39:968–71. - PubMed
-
- Weedon KM, Rupp AH, Heffron AC, et al. . The impact of infection control upon hospital-acquired influenza and respiratory syncytial virus. Scand J Infect Dis 2013; 45:297–303. - PubMed
-
- Hei H, Bezpalko O, Smathers SA, et al. . Development of a novel prevention bundle for pediatric healthcare-associated viral infections. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2018; 39:1086–92. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

