Commissioning and performance characteristics of a pre-clinical image-guided radiotherapy system
- PMID: 30989595
- PMCID: PMC6557883
- DOI: 10.1007/s13246-019-00755-4
Commissioning and performance characteristics of a pre-clinical image-guided radiotherapy system
Abstract
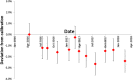
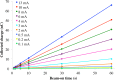
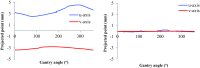
Characteristics of a small-animal radiotherapy device, the X-RAD SmART, are described following commissioning of the device for pre-clinical radiotherapy research. Performance characteristics were assessed using published standards and compared with previous results published for similar systems. Operational radiation safety was established. Device X-ray beam quality and output dose-rate were found to be consistent with those reported for similar devices. Output steadily declined over 18 months though remained within tolerance levels. There is considerable variation in output factor across the international installations for the smallest field size (varying by more than 30% for 2.5 mm diameter fields). Measured depth dose and profile data was mostly consistent with that published, with some differences in penumbrae and generally reduced flatness. Target localisation is achieved with an imaging panel and with automatic corrections for panel flex and device mechanical instability, targeting within 0.2 mm is achievable. The small-animal image-guided radiotherapy platform has been implemented and assessed and found to perform as specified. The combination of kV energy and high spatial precision make it suitable for replicating clinical dose distributions at the small-animal scale, though dosimetric uncertainties for the narrowest fields need to be acknowledged.
Keywords: Commissioning; Dose delivery; Image guidance; Pre-clinical; Small animal radiotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Multi-institutional dosimetric and geometric commissioning of image-guided small animal irradiators.Med Phys. 2014 Mar;41(3):031714. doi: 10.1118/1.4866215. Med Phys. 2014. PMID: 24593718
-
Commissioning and initial stereotactic ablative radiotherapy experience with Vero.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2014 Mar 6;15(2):4685. doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v15i2.4685. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2014. PMID: 24710458 Free PMC article.
-
Two-dimensional inverse planning and delivery with a preclinical image guided microirradiator.Med Phys. 2013 Oct;40(10):101709. doi: 10.1118/1.4819935. Med Phys. 2013. PMID: 24089899
-
A review of treatment planning for precision image-guided photon beam pre-clinical animal radiation studies.Z Med Phys. 2014 Dec;24(4):323-34. doi: 10.1016/j.zemedi.2014.02.004. Epub 2014 Mar 12. Z Med Phys. 2014. PMID: 24629309 Review.
-
Intraoperative radiation therapy with 50 kV x-rays: A multi-institutional review.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024 Mar;25(3):e14272. doi: 10.1002/acm2.14272. Epub 2024 Jan 26. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 38279520 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Veliparib Is an Effective Radiosensitizing Agent in a Preclinical Model of Medulloblastoma.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Apr 29;8:633344. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.633344. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33996894 Free PMC article.
-
The importance of standardization and challenges of dosimetry in conventional preclinical radiation biology research.Br J Radiol. 2025 Jul 1;98(1171):993-1004. doi: 10.1093/bjr/tqaf066. Br J Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40127177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of radiochromic gel dosimetry to commissioning of a megavoltage research linear accelerator for small-field animal irradiation studies.Med Phys. 2021 Mar;48(3):1404-1416. doi: 10.1002/mp.14685. Epub 2021 Feb 6. Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 33378092 Free PMC article.
-
Conventional Therapies Deplete Brain-Infiltrating Adaptive Immune Cells in a Mouse Model of Group 3 Medulloblastoma Implicating Myeloid Cells as Favorable Immunotherapy Targets.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 3;13:837013. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.837013. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35309309 Free PMC article.
-
Fractionated low-dose radiotherapy primes the tumor microenvironment for immunotherapy in a murine mesothelioma model.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2025 Jan 3;74(2):44. doi: 10.1007/s00262-024-03889-x. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2025. PMID: 39751851 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

