Sestrin modulator NV-5138 produces rapid antidepressant effects via direct mTORC1 activation
- PMID: 30990795
- PMCID: PMC6546461
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI126859
Sestrin modulator NV-5138 produces rapid antidepressant effects via direct mTORC1 activation
Abstract
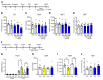
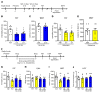
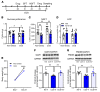
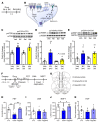
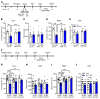
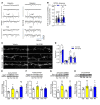
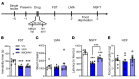
Preclinical studies demonstrate that rapid acting antidepressants, including ketamine require stimulation of mTORC1 signaling. This pathway is regulated by neuronal activity, endocrine and metabolic signals, notably the amino acid leucine, which activates mTORC1 signaling via binding to the upstream regulator sestrin. Here, we examined the antidepressant actions of NV-5138, a novel highly selective small molecule modulator of sestrin that penetrates the blood brain barrier. The results demonstrate that a single dose of NV-5138 produced rapid and long-lasting antidepressant effects, and rapidly reversed anhedonia caused by chronic stress exposure. The antidepressant actions of NV-5138 required BDNF release as the behavioral responses are blocked by infusion of a BDNF neutralizing antibody into the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) or in mice with a knock-in of a BDNF polymorphism that blocks activity dependent BDNF release. NV-5138 administration also rapidly increased synapse number and function in the mPFC, and reversed the synaptic deficits caused by chronic stress. Together, the results demonstrate that NV-5138 produced rapid synaptic and antidepressant behavioral responses via activation of the mTORC1 pathway and BDNF signaling, indicating that pharmacological modulation of sestrin is a novel approach for development of rapid acting antidepressants.
Keywords: Depression; Neuroscience.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
NV-5138 as a fast-acting antidepressant via direct activation of mTORC1 signaling.J Clin Invest. 2019 May 20;129(6):2207-2209. doi: 10.1172/JCI129702. eCollection 2019 May 20. J Clin Invest. 2019. PMID: 31107245 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

