Next-Generation Hedgehog/GLI Pathway Inhibitors for Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 30991683
- PMCID: PMC6520835
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers11040538
Next-Generation Hedgehog/GLI Pathway Inhibitors for Cancer Therapy
Abstract
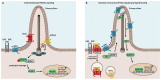
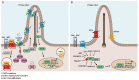
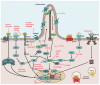
The Hedgehog/Glioma-associated oncogene homolog (HH/GLI) signaling pathway regulates self-renewal of rare and highly malignant cancer stem cells (CSC), which have been shown to account for the initiation and maintenance of tumor growth as well as for drug resistance, metastatic spread and relapse. Efficacious therapeutic approaches targeting CSC pathways, such as HH/GLI signaling in combination with chemo, radiation or immunotherapy are, therefore, of high medical need. Pharmacological inhibition of HH/GLI pathway activity represents a promising approach to eliminate malignant CSC. Clinically approved HH/GLI pathway inhibitors target the essential pathway effector Smoothened (SMO) with striking therapeutic efficacy in skin and brain cancer patients. However, multiple genetic and molecular mechanisms resulting in de novo and acquired resistance to SMO inhibitors pose major limitations to anti-HH/GLI therapies and, thus, the eradication of CSC. In this review, we summarize reasons for clinical failure of SMO inhibitors, including mechanisms caused by genetic alterations in HH pathway effectors or triggered by additional oncogenic signals activating GLI transcription factors in a noncanonical manner. We then discuss emerging novel and rationale-based approaches to overcome SMO-inhibitor resistance, focusing on pharmacological perturbations of enzymatic modifiers of GLI activity and on compounds either directly targeting oncogenic GLI factors or interfering with synergistic crosstalk signals known to boost the oncogenicity of HH/GLI signaling.
Keywords: GLI transcription factors; Hedgehog signaling; Smoothened inhibitors; cancer stem cells; drug resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

