Nicotinic Acid Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate (NAADP) Induces Intracellular Ca2+ Release through the Two-Pore Channel TPC1 in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Cells
- PMID: 30991693
- PMCID: PMC6521149
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers11040542
Nicotinic Acid Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate (NAADP) Induces Intracellular Ca2+ Release through the Two-Pore Channel TPC1 in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Cells
Abstract
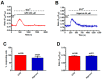
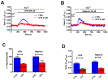
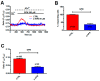
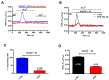
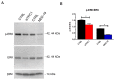
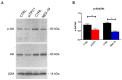
Nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NAADP) gates two-pore channels 1 and 2 (TPC1 and TPC2) to elicit endo-lysosomal (EL) Ca2+ release. NAADP-induced EL Ca2+ signals may be amplified by the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) through the Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release mechanism (CICR). Herein, we aimed at assessing for the first time the role of EL Ca2+ signaling in primary cultures of human metastatic colorectal carcinoma (mCRC) by exploiting Ca2+ imaging and molecular biology techniques. The lysosomotropic agent, Gly-Phe β-naphthylamide (GPN), and nigericin, which dissipates the ΔpH which drives Ca2+ refilling of acidic organelles, caused massive Ca2+ release in the presence of a functional inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate (InsP₃)-sensitive ER Ca2+ store. Liposomal delivery of NAADP induced a transient Ca2+ release that was reduced by GPN and NED-19, a selective TPC antagonist. Pharmacological and genetic manipulations revealed that the Ca2+ response to NAADP was triggered by TPC1, the most expressed TPC isoform in mCRC cells, and required ER-embedded InsP₃ receptors. Finally, NED-19 and genetic silencing of TPC1 reduced fetal calf serum-induced Ca2+ signals, proliferation, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase and Akt phoshorylation in mCRC cells. These data demonstrate that NAADP-gated TPC1 could be regarded as a novel target for alternative therapies to treat mCRC.
Keywords: NAADP; TPC1; cancer; colorectal carcinoma; lysosomal Ca2+ signalling; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nicotinic Acid Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate Induces Intracellular Ca2+ Signalling and Stimulates Proliferation in Human Cardiac Mesenchymal Stromal Cells.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Mar 15;10:874043. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.874043. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35392169 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate activates two-pore channel TPC1 to mediate lysosomal Ca2+ release in endothelial colony-forming cells.J Cell Physiol. 2021 Jan;236(1):688-705. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29896. Epub 2020 Jun 24. J Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 32583526
-
NAADP mobilizes calcium from acidic organelles through two-pore channels.Nature. 2009 May 28;459(7246):596-600. doi: 10.1038/nature08030. Epub 2009 Apr 22. Nature. 2009. PMID: 19387438 Free PMC article.
-
Endolysosomal Ca2+ Signalling and Cancer Hallmarks: Two-Pore Channels on the Move, TRPML1 Lags Behind!Cancers (Basel). 2018 Dec 27;11(1):27. doi: 10.3390/cancers11010027. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30591696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calcium signaling via two-pore channels: local or global, that is the question.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010 Mar;298(3):C430-41. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00475.2009. Epub 2009 Dec 16. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20018950 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NAADP-induced intracellular calcium ion is mediated by the TPCs (two-pore channels) in hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Aug;25(15):7485-7499. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16783. Epub 2021 Jul 15. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34263977 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive Oxygen Species and Endothelial Ca2+ Signaling: Brothers in Arms or Partners in Crime?Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 10;22(18):9821. doi: 10.3390/ijms22189821. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34575985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Endolysosomal Two-Pore Channels to Treat Cardiovascular Disorders in the Novel COronaVIrus Disease 2019.Front Physiol. 2021 Jan 26;12:629119. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.629119. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33574769 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotinic Acid Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate Induces Intracellular Ca2+ Signalling and Stimulates Proliferation in Human Cardiac Mesenchymal Stromal Cells.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Mar 15;10:874043. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.874043. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35392169 Free PMC article.
-
The human amniotic fluid stem cell secretome triggers intracellular Ca2+ oscillations, NF-κB nuclear translocation and tube formation in human endothelial colony-forming cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Aug;25(16):8074-8086. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16739. Epub 2021 Jul 20. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34288391 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zuccolo E., Di Buduo C., Lodola F., Orecchioni S., Scarpellino G., Kheder D.A., Poletto V., Guerra G., Bertolini F., Balduini A., et al. Stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha promotes endothelial colony-forming cell migration through the Ca(2+)-dependent activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT pathways. Stem Cells Dev. 2018;27:23–34. doi: 10.1089/scd.2017.0114. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cardenas C., Muller M., McNeal A., Lovy A., Jana F., Bustos G., Urra F., Smith N., Molgo J., Diehl J.A., et al. Selective vulnerability of cancer cells by inhibition of Ca(2+) transfer from endoplasmic reticulum to mitochondria. Cell Rep. 2016;15:219–220. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.03.045. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
- Dipartimenti di Eccellenza Program (2018-2022) - Dept. of Biology and Biotechnology "L. Spallanzani"/Ministero dell'Istruzione, dell'Università e della Ricerca
- Fondo Ricerca Giovani/Università degli Studi di Pavia
- RF-2010-2316319/Ministero della Salute
- RC/08059815B/Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo
- RF-2011-02352315/Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

