Protective Effects of Moderate Ca Supplementation against Cd-Induced Bone Damage under Different Population-Relevant Doses in Young Female Rats
- PMID: 30991710
- PMCID: PMC6521033
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11040849
Protective Effects of Moderate Ca Supplementation against Cd-Induced Bone Damage under Different Population-Relevant Doses in Young Female Rats
Abstract
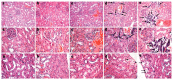
Estimation of the skeleton-protective effects of Ca in Cd-induced bone damage is helpful in the assessment of Cd health risk. The aim of this study was to identify whether Ca supplementation during exposure to different population-relevant doses of Cd can prevent Cd-induced bone damage under the tolerable upper intake level of Ca supplementation. Young female Sprague-Dawley rats were given different population-relevant doses of Cd (1, 5, and 50 mg Cd/kg diet) and Ca supplementation (0.4% Ca supplementation) intervention. Ca supplementation significantly decreased Cd-induced bone microstructure damage, increased bone biomechanics (p < 0.05), serum bone formation marker level (p < 0.05) and expression of osteogenic gene markers exposure to the 5 and 50 mg Cd/kg diets. However, it had no impact on these indicators under the 1 mg Cd/kg diets, with the exception of expression of osteogenic marker genes. Ca supplementation significantly decreased serum Klotho level (p < 0.05), and fibroblast growth factor 23/Klotho-associated gene expression in the kidney and bone showed significant changes. In conclusion, Ca supplementation has a positive effect on bone formation and bone quality against the damaging impact of Cd, especially with exposure to the 5 mg and 50 mg Cd/kg diet, which may be related to its impact on the fibroblast growth factor 23/Klotho axis.
Keywords: bone; cadmium; calcium; fibroblast growth factor 23; klotho.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
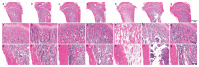
Similar articles
-
The Preventive Impact of Chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa L.) Extract Regarding the Disruption of Calcium and Phosphorus Homeostasis and Chosen Pathways of Its Regulation in an Animal Model of General Population Exposure to Cadmium.Nutrients. 2025 Feb 16;17(4):702. doi: 10.3390/nu17040702. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40005030 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Dietary Calcium Supplementation on Bone Metabolism, Kidney Mineral Concentrations, and Kidney Function in Rats Fed a High-Phosphorus Diet.J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2015;61(2):195-200. doi: 10.3177/jnsv.61.195. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2015. PMID: 26052152
-
The effects of Mg supplementation in diets with different calcium levels on the bone status and bone metabolism in growing female rats.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2013 Dec;155(3):431-8. doi: 10.1007/s12011-013-9798-1. Epub 2013 Sep 18. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2013. PMID: 24046258
-
Klotho/FGF23 and Wnt Signaling as Important Players in the Comorbidities Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Mar 16;12(3):185. doi: 10.3390/toxins12030185. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32188018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of klotho deletion from bone during chronic kidney disease.Bone. 2017 Jul;100:50-55. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2017.02.006. Epub 2017 Feb 20. Bone. 2017. PMID: 28232146 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Curative Potential of Substances with Bioactive Properties to Alleviate Cd Toxicity: A Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Sep 28;19(19):12380. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191912380. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36231680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Preventive Impact of Chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa L.) Extract Regarding the Disruption of Calcium and Phosphorus Homeostasis and Chosen Pathways of Its Regulation in an Animal Model of General Population Exposure to Cadmium.Nutrients. 2025 Feb 16;17(4):702. doi: 10.3390/nu17040702. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40005030 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Klotho in Living Kidney Donors and Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Meta-Analysis.J Clin Med. 2020 Jun 12;9(6):1834. doi: 10.3390/jcm9061834. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32545510 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Calcium and Annatto Tocotrienol Supplementation on Bone Loss Induced by Pantoprazole in Male Rats.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020 Jul 2;14:2561-2572. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S260565. eCollection 2020. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020. PMID: 32753839 Free PMC article.
References
-
- European Food Safety Authority Cadmium dietary exposure in the European population. EFSA J. 2012;10:2551. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2012.2551. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

