Preparation and Evaluation of Topically Applied Azithromycin Based on Sodium Hyaluronate in Treatment of Conjunctivitis
- PMID: 30991749
- PMCID: PMC6523157
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11040183
Preparation and Evaluation of Topically Applied Azithromycin Based on Sodium Hyaluronate in Treatment of Conjunctivitis
Abstract
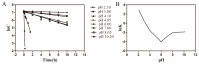
Azithromycin (AZI) eye drops containing sodium hyaluronate (SH) were developed to improve the bioavailability of AZI. Interaction between AZI and SH in the AZI-SH formulation was investigated by differential scanning calorimetry, X-ray diffraction, and ¹H-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy analyses. Moreover, advantages of using SH as an excipient were investigated by comparing physiological properties and pharmacokinetic behaviors of SH-containing AZI eye drops with that of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC)-containing formulation. In addition, safety of the developed AZI-SH eye drops was evaluated by in vitro 3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-Thiazyl)-2, 5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide assay (MTT assay) and neutral red uptake assay as well as in vivo eye irritation test and acute toxicity test. The results indicated that AZI formed a complex with SH under a slightly acidic condition. The area under the curve (AUC) of AZI in SH-containing formulation was 1.58-fold higher (P<0.01) than that in HPMC-containing formulation due to the interaction between the amine group of AZI and the carboxyl group of SH, despite of the higher viscosity of HPMC-containing formulation. Safety evaluation showed that AZI-SH eye drops caused no obvious eye irritation and acute toxicity. In conclusion, the developed SH-containing AZI formulation possessing advantages of longer retention time and higher drug availability was a promising drug formulation for topical ocular therapy.
Keywords: azithromycin; bioadhesion; eye drops; ocular bioavailability; safety evaluation; sodium hyaluronate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Liu F., Porco T.C., Mkocha H.A., Muñoz B., Ray K.J., Bailey R.L., Lietman T.M., West S.K. The efficacy of oral azithromycin in clearing ocular chlamydia: Mathematical modeling from a community-randomized trachoma trial. Epidemics. 2014;6:10–17. doi: 10.1016/j.epidem.2013.12.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

