Asymptomatic Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: Insights from Population-Based Studies
- PMID: 30991799
- PMCID: PMC6549070
- DOI: 10.5853/jos.2018.03608
Asymptomatic Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: Insights from Population-Based Studies
Abstract
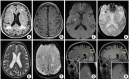
Cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD) is a common group of neurological conditions that confer a significant burden of morbidity and mortality worldwide. In most cases, CSVD is only recognized in its advanced stages once its symptomatic sequelae develop. However, its significance in asymptomatic healthy populations remains poorly defined. In population-based studies of presumed healthy elderly individuals, CSVD neuroimaging markers including white matter hyperintensities, lacunes, cerebral microbleeds, enlarged perivascular spaces, cortical superficial siderosis, and cerebral microinfarcts are frequently detected. While the presence of these imaging markers may reflect unique mechanisms at play, there are likely shared pathways underlying CSVD. Herein, we aim to assess the etiology and significance of these individual biomarkers by focusing in asymptomatic populations at an epidemiological level. By primarily examining population-based studies, we explore the risk factors that are involved in the formation and progression of these biomarkers. Through a critical semi-systematic review, we aim to characterize "asymptomatic" CSVD, review screening modalities, and draw associations from observational studies in clinical populations. Lastly, we highlight areas of research (including therapeutic approaches) in which further investigation is needed to better understand asymptomatic CSVD.
Keywords: Cerebral small vessel diseases; Epidemiology; Leukoaraiosis; Stroke, lacunar.
Figures
References
-
- Berkhemer OA, Fransen PS, Beumer D, van den Berg LA, Lingsma HF, Yoo AJ, et al. A randomized trial of intraarterial treatment for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:11–20. - PubMed
-
- Campbell BC, Mitchell PJ, Kleinig TJ, Dewey HM, Churilov L, Yassi N, et al. Endovascular therapy for ischemic stroke with perfusion-imaging selection. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:1009–1018. - PubMed
-
- Jovin TG, Chamorro A, Cobo E, de Miquel MA, Molina CA, Rovira A, et al. Thrombectomy within 8 hours after symptom onset in ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:2296–2306. - PubMed
-
- Saver JL, Goyal M, Bonafe A, Diener HC, Levy EI, Pereira VM, et al. Stent-retriever thrombectomy after intravenous t-PA vs. t-PA alone in stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:2285–2295. - PubMed
-
- Bracard S, Ducrocq X, Mas JL, Soudant M, Oppenheim C, Moulin T, et al. Mechanical thrombectomy after intravenous alteplase versus alteplase alone after stroke (THRACE): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15:1138–1147. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

