Interleukin-35 modulates the balance between viral specific CD4+CD25+CD127dim/- regulatory T cells and T helper 17 cells in chronic hepatitis B virus infection
- PMID: 30992023
- PMCID: PMC6469219
- DOI: 10.1186/s12985-019-1158-0
Interleukin-35 modulates the balance between viral specific CD4+CD25+CD127dim/- regulatory T cells and T helper 17 cells in chronic hepatitis B virus infection
Abstract
Background: Interleukin (IL)-35 regulates imbalance between regulatory T cells (Tregs) and T helper (Th) 17 cells, leading to an important modulator in autoimmune disorder, cancer, and infectious diseases. Our previous study revealed an immunosuppressive activity of IL-35 in chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. Thus, the aim of the current study was to investigate the role of regulatory function of IL-35 to viral specific Tregs/Th17 cells balance in chronic HBV infection.
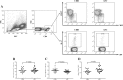
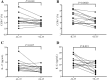
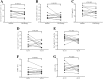
Methods: A total of 44 HLA-A2 restricted chronic HBV infected patients, including 21 of chronic hepatitis B (CHB) and 23 of asymptomatic HBV carriers (ASC) were enrolled. Purified CD4+ T cells or CD4+CD25+CD127dim/- Tregs were stimulated with recombinant IL-35. HBV core antigen specific Tregs and Th17 cells were determined by flow cytometry. FoxP3 and RORγt mRNA was measured by real-time PCR. Cytokines production (IL-10 and IL-17) was investigated by ELISA.
Results: Peripheral viral specific Tregs was comparable between CHB and ASC. However, increased percentage of viral specific Th17 cells was found in CHB, leading to the reduction of Tregs/Th17 ratio in CHB patients. IL-35 stimulation elevated viral specific Tregs, but not Th17 cells frequency, in both CHB and ASC, resulting in the elevation of Tregs/Th17 ratio in both groups. This process was accompanied by increased expression of FoxP3 mRNA and IL-10 production, and decreased IL-17 secretion and STAT3 phosphorylation in purified CD4+ T cells. Moreover, IL-35 stimulation inhibited viral specific Th17-like phenotype differentiation from Tregs in CHB patients. Effective anti-HBV therapy did not affect viral specific Tregs/Th17 cells frequency or IL-35 expression in CHB patients, however, reduced responsiveness of CD4+ T cells or Tregs to IL-35 stimulation in vitro.
Conclusion: Our findings indicated that IL-35 regulation to viral specific Tregs/Th17 balance may contribute to viral persistence in chronic HBV infection.
Keywords: Hepatitis B virus; Interleukin-35; Regulatory T cells; T helper 17 cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of The Second Hospital of Jilin University on March 2017.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interleukin-35 Suppresses Antiviral Immune Response in Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Nov 13;7:472. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00472. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29181338 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased CD4+CD25+CD127dim/- Regulatory T Cells and T Helper 17 Cell Responsiveness to Toll-Like Receptor 2 in Chronic Hepatitis C Patients with Daclatasvir Plus Asunaprevir Therapy.Viral Immunol. 2018 Oct;31(8):559-567. doi: 10.1089/vim.2018.0055. Epub 2018 Aug 1. Viral Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30067145
-
Interleukin-21 modulates balance between regulatory T cells and T-helper 17 cells in chronic hepatitis B virus infection.BMC Infect Dis. 2023 Oct 24;23(1):719. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08723-w. BMC Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37875903 Free PMC article.
-
Restoring homeostasis of CD4⁺ T cells in hepatitis-B-virus-related liver fibrosis.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Oct 14;21(38):10721-31. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i38.10721. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26478664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Relationship between CD4+CD25+Treg cells, Th17 cells and IL-6 and the prognosis of hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure: a meta-analysis].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2014 Jul;22(7):493-8. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2014.07.004. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25203799 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Reduced circulating interleukin 35 is associated with enhanced peripheral T cell function in primary biliary cholangitis.Biomol Biomed. 2023 Mar 16;23(2):248-258. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.2022.8147. Biomol Biomed. 2023. PMID: 36314719 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-35 has a Protective Role in Infectious Mononucleosis-Induced Liver Inflammation Probably by Inhibiting CD8+ T Cell Function.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2022 Oct 11;70(1):25. doi: 10.1007/s00005-022-00663-8. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2022. PMID: 36219249
-
The Role of IL-35 in the Pathophysiological Processes of Liver Disease.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jan 21;11:569575. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.569575. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33584256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin 35 Regulatory B Cells.J Mol Biol. 2021 Jan 8;433(1):166607. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2020.07.019. Epub 2020 Aug 2. J Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 32755620 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytokines and Chemokines in HBV Infection.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Dec 2;8:805625. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.805625. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34926586 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

