Microfluidic multipoles theory and applications
- PMID: 30992450
- PMCID: PMC6467910
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-09740-7
Microfluidic multipoles theory and applications
Abstract
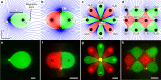
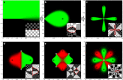
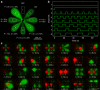
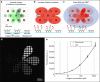
Microfluidic multipoles (MFMs) have been realized experimentally and hold promise for "open-space" biological and chemical surface processing. Whereas convective flow can readily be predicted using hydraulic-electrical analogies, the design of advanced microfluidic multipole is constrained by the lack of simple, accurate models to predict mass transport within them. In this work, we introduce the complete solutions to mass transport in multipolar microfluidics based on the iterative conformal mapping of 2D advection-diffusion around a simple edge into dipoles and multipolar geometries, revealing a rich landscape of transport modes. The models are validated experimentally with a library of 3D printed devices and found in excellent agreement. Following a theory-guided design approach, we further ideate and fabricate two classes of spatiotemporally reconfigurable multipolar devices that are used for processing surfaces with time-varying reagent streams, and to realize a multistep automated immunoassay. Overall, the results set the foundations for exploring, developing, and applying open-space microfluidic multipoles.
Conflict of interest statement
T.G., P.A.G., and E.B. declare a competing financial interest under the form of a patent pending in the US. The patent application covers the rMFM and the tMFM geometries of microfluidic multipoles. Patent application number 62739685. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Delamarche, E. & Kaigala, G. V. Open-Space Microfluidics: Concepts, Implementations, Applications. (Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, Germany 2018).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

