Pain management in patients with cirrhosis
- PMID: 30992804
- PMCID: PMC6385960
- DOI: 10.1002/cld.711
Pain management in patients with cirrhosis
Figures
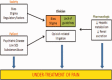
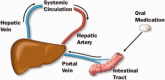
References
-
- Larson AM, Polson J, Fontana RJ, Davern TJ, Lalani E, Hynan LS, et al.; Acute Liver Failure Study Group . Acetaminophen‐induced acute liver failure: results of a United States multicenter, prospective study. Hepatology 2005;42:1364‐1372. - PubMed
-
- Doğan S, Ozberk S, Yurci A. Pregabalin‐induced hepatotoxicity. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011;23:628. - PubMed
-
- Bosilkovska M, Walder B, Besson M, Daali Y, Desmeules J. Analgesics in patients with hepatic impairment: pharmacology and clinical implications. Drugs 2012;72:1645‐1669. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

