Treatment of alcoholic hepatitis
- PMID: 30992831
- PMCID: PMC6448618
- DOI: 10.1002/cld.166
Treatment of alcoholic hepatitis
Figures


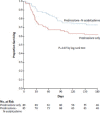

References
-
- Kamath PS, Wiesner RH, Malinchoc M, Kremers W, Therneau TM, Kosberg CL, et al. A model to predict survival in patients with end‐stage liver disease. Hepatology 2001; 33: 464–470. - PubMed
-
- Dominguez M, Rincòn D, Abraldes JG, Miquel R, Colmenero J, Bellot P, et al. A new scoring system for prognostic stratification of patients with alcoholic hepatitis. Am J Gastroenterol 2008; 103: 2747–2756. - PubMed
-
- Louvet A, Wartel F, Castel H, Dharancy S, Hollebecque A, Canva‐Delcambre V, et al. Infection in patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis treated with steroids: early response to therapy is the key factor. Gastroenterology 2009; 137: 541–548. - PubMed
-
- Mendenhall CL, Moritz TE, Roselle GA, Morgan TR, Nemchausky BA, Tamburro CH, et al. Protein energy malnutrition in severe alcoholic hepatitis: diagnosis and response to treatment. The VA Cooperative Study Group #275. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 1995; 19: 258–265. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

