Acetaminophen overdose: What practitioners need to know
- PMID: 30992913
- PMCID: PMC6448726
- DOI: 10.1002/cld.373
Acetaminophen overdose: What practitioners need to know
Figures
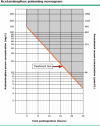
References
-
- Nourjah P, Ahmad SR, Karwoski C, Willy M. Estimates of acetaminophen (Paracetomal)‐associated overdoses in the United States. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 2006;15(6):398‐405. - PubMed
-
- Larson AM, Polson J, Fontana RJ, et al. Acetaminophen‐induced acute liver failure: results of a United States multicenter, prospective study. Hepatology 2005;42(6):1364‐1372. - PubMed
-
- Smilkstein MJ, Knapp GL, Kulig KW, Rumack BH. Efficacy of oral N‐acetylcysteine in the treatment of acetaminophen overdose. N Engl J Med 1988;319:1557‐1562. - PubMed
-
- Davern TJ, James LP, Hinson JA, et al. Measurement of serum acetaminophen–protein adducts in patients with acute liver failure. Gastroenterology 2006;130:687‐694. - PubMed

