Update on primary sclerosing cholangitis
- PMID: 30992971
- PMCID: PMC6467155
- DOI: 10.1002/cld.633
Update on primary sclerosing cholangitis
Figures
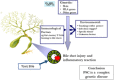
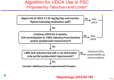
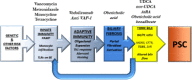
References
-
- Williamson KD, Chapman RW. Primary sclerosing cholangitis: a clinical update. Brit Med Bull 2015;114:53–64. - PubMed
-
- Boonstra KB, Weersma RK, van Erpecum KJ, Rauws EA, Spanier BW, Poen AC, et al.; EpiPSCPBC Study Group . Population‐based epidemiology, malignancy risk, and outcome of primary sclerosing cholangitis. Hepatology 2013;58:2045–2055. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

