Characterization of PPIB interaction in the P3H1 ternary complex and implications for its pathological mutations
- PMID: 30993352
- PMCID: PMC11105654
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-019-03102-8
Characterization of PPIB interaction in the P3H1 ternary complex and implications for its pathological mutations
Abstract
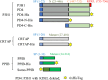
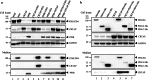
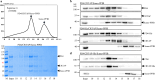
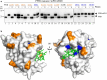
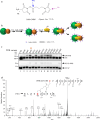
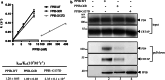
The P3H1/CRTAP/PPIB complex is essential for prolyl 3-hydroxylation and folding of procollagens in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Deficiency in any component of this ternary complex is associated with the misfolding of collagen and the onset of osteogenesis imperfecta. However, little structure information is available about how this ternary complex is assembled and retained in the ER. Here, we assessed the role of the KDEL sequence of P3H1 and probed the spatial interactions of PPIB in the complex. We show that the KDEL sequence is essential for retaining the P3H1 complex in the ER. Its removal resulted in co-secretion of P3H1 and CRTAP out of the cell, which was mediated by the binding of P3H1 N-terminal domain with CRTAP. The secreted P3H1/CRTAP can readily bind PPIB with their C-termini close to PPIB in the ternary complex. Cysteine modification, crosslinking, and mass spectrometry experiments identified PPIB surface residues involved in the complex formation, and showed that the surface of PPIB is extensively covered by the binding of P3H1 and CRTAP. Most importantly, we demonstrated that one disease-associated pathological PPIB mutation on the binding interface did not affect the PPIB prolyl-isomerase activity, but disrupted the formation of P3H1/CRTAP/PPIB ternary complex. This suggests that defects in the integrity of the P3H1 ternary complex are associated with pathological collagen misfolding. Taken together, these results provide novel structural information on how PPIB interacts with other components of the P3H1 complex and indicate that the integrity of P3H1 complex is required for proper collagen formation.
Keywords: Chaperone; Hydroxylase; Hyperelastosis cutis; Osteogenesis imperfecta; Sulfo-GMBS.
Figures

References
-
- Bächinger HP, Mizuno K, Vranka JA, Boudko SP. Collagen formation and structure. In: Mander L, Liu HW, editors. Comprehensive natural products II: chemistry and biology. Oxford: Elsevier; 2010. pp. 469–530.
-
- Myllyharju J. Intracellular post-translational modifications of collagens. Top Curr Chem. 2005;247:115–147. doi: 10.1007/b103821. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

