Arginine within a specific motif near the N-terminal of FimY is critical for the maximal production of type 1 fimbriae in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium
- PMID: 30993839
- PMCID: PMC6741139
- DOI: 10.1002/mbo3.846
Arginine within a specific motif near the N-terminal of FimY is critical for the maximal production of type 1 fimbriae in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium
Abstract
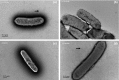
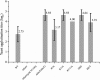
An important Salmonella serovar for both human and animals Salmonella Typhimurium possesses 13 gene clusters that have the potential to produce fimbrial structure, among which the type 1 fimbriae with the binding specificity to mannose residue is the most commonly found type. Six structural genes and five regulatory genes comprise the fim gene cluster that is responsible for the production of type 1 fimbriae in S. Typhimurium. The fimY gene encodes a positive regulator for type 1 fimbrial expression since a deletion in fimY abolished the production of fimbriae. The N-terminal portion of FimY contains amino acid residues that exhibit some similarity as those found in the proteins possessing the PilZ domain, which is engaged in cyclic di-GMP binding. A fimY allele that had a change from arginine to alanine at position 7 (R7A) or 7 and 11 (R7/11A) generated by site-directed mutagenesis in a 6 RRERH11 R motif near N-terminal, when cloned in pACYC184 and transformed into a fimY-deleted strain, decreased the expression of fimA and fimZ. The number of type 1 fimbriae in these two transformants was also less than those of the other transformants that contained different fimY alleles in pACYC184 when observed in electron microscopy. However, changing from arginine to alanine at position 11 (R11A) remained the same as the wild-type fimY allele. It is likely that the arginine at the 7th position of FimY is critical for its maximal activating activity upon fimZ. Another motif 83 DI85 SLWIEK91 G motif did not affect the function of FimY. Although FimY has the two aforementioned motifs, which contain some amino acids that are present within those of the PilZ domain proteins, secondary structure prediction analysis did not reveal that FimY has a conformation commonly observed in PilZ-like proteins. Therefore, FimY and PilZ domain proteins are not homologs. Further investigation for a detailed analysis of FimY is thus warranted.
Keywords: fimY; PilZ domain; Salmonella Typhimurium; type 1 fimbriae.
© 2019 The Authors. MicrobiologyOpen published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
FimY of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium functions as a DNA-binding protein and binds the fimZ promoter.Microbiol Res. 2014 Jul-Aug;169(7-8):496-503. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2013.12.006. Epub 2013 Dec 30. Microbiol Res. 2014. PMID: 24462182
-
Control of FimY translation and type 1 fimbrial production by the arginine tRNA encoded by fimU in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Mol Microbiol. 2001 May;40(3):757-68. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02430.x. Mol Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11359580
-
Characterization of FimY as a coactivator of type 1 fimbrial expression in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Infect Immun. 2000 Jun;68(6):3305-13. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.6.3305-3313.2000. Infect Immun. 2000. PMID: 10816478 Free PMC article.
-
FimY does not interfere with FimZ-FimW interaction during type 1 fimbria production by Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Infect Immun. 2013 Dec;81(12):4453-60. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00795-13. Epub 2013 Sep 16. Infect Immun. 2013. PMID: 24042120 Free PMC article.
-
A previously uncharacterized gene stm0551 plays a repressive role in the regulation of type 1 fimbriae in Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium.BMC Microbiol. 2012 Jun 20;12:111. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-12-111. BMC Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22716649 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Type 1 fimbria and P pili: regulatory mechanisms of the prototypical members of the chaperone-usher fimbrial family.Arch Microbiol. 2024 Aug 10;206(9):373. doi: 10.1007/s00203-024-04092-3. Arch Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39127787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting effect of berberine on type I fimbriae of Salmonella Typhimurium and its effective inhibition of biofilm.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Feb;105(4):1563-1573. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11116-1. Epub 2021 Jan 26. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33496815
References
-
- CDC (2011). National salmonella surveillance overview. Atlanta: US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

