Physical Activity and Mobile Phone Apps in the Preschool Age: Perceptions of Teachers and Parents
- PMID: 30994465
- PMCID: PMC6492065
- DOI: 10.2196/12512
Physical Activity and Mobile Phone Apps in the Preschool Age: Perceptions of Teachers and Parents
Abstract
Background: Physical activity (PA) is already beneficial at the preschool age. In many countries, young children spend most of their days in the preschool setting, making it a common arena for PA interventions. Mobile health tools are becoming increasingly popular to promote PA in different populations; however, little is known about the interest for and how the preschool setting could incorporate such a tool.
Objective: This study aimed to examine how teachers and parents perceive PA in preschool-aged children in general and their perceptions of how a mobile phone app could be used to promote PA in the preschool setting.
Methods: Semistructured interviews were conducted with 15 teachers (93%, [14/15] women, mean age 43.5 years, 47%, [7/15] with a university degree and 10 parents [91%, 9/10] women, mean age 38.9 years, all with a university degree) recruited from 2 urban preschools in central Sweden. The interviews were recorded, fully transcribed, coded, and analyzed using thematic analysis by means of an inductive approach.
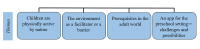
Results: The analysis revealed 4 themes: (1) children are physically active by nature, (2) the environment as a facilitator or a barrier, (3) prerequisites of the adult world, and (4) an app in the preschool setting-challenges and possibilities. Parents and teachers perceived preschoolers as being spontaneously physically active; however, high-intensity PA was perceived as low. The PA was specifically performed during the day in the preschool. Identified facilitators of PA were access to safe and engaging outdoor environments such as forests, spacious indoor areas, and adult involvement. Adult involvement was considered especially important for children preferring sedentary activities. Identified barriers for PA were restricted indoor and outdoor space, rules for indoor activities, and lack of adult involvement because of time constraints. The teachers perceived that they had limited skills and experiences using apps in general, although they also acknowledged the increasing role of technological tools in the curriculum. Thus, the teachers expressed an interest for an app designed as a support tool for them, especially for situations when PA was limited because of perceived barriers. They suggested the app to include accessible information regarding the health benefits of PA in children linked to a library of activities for different settings and seasons. Parents suggested interactive app features including problem-solving tasks and music and dance, but not video clips as they made children passive.
Conclusions: Vigorous PA was perceived as low in preschool-aged children. Future tailoring of interventions in the preschool setting should work around barriers and support facilitators to PA, especially PA of high intensity. In such work, an app could serve as a source of inspiration for PA in different ages, settings, and seasons and thus reduce environmental and structural inequalities in the preschool setting.
Keywords: child, preschool; mHealth; parents; physical activity; qualitative research; school teachers.
©Anna Ek, Johanna Sandborg, Christine Delisle Nyström, Anna-Karin Lindqvist, Stina Rutberg, Marie Löf. Originally published in JMIR Mhealth and Uhealth (http://mhealth.jmir.org), 17.04.2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Carson V, Lee EY, Hewitt L, Jennings C, Hunter S, Kuzik N, Stearns JA, Unrau SP, Poitras VJ, Gray C, Adamo KB, Janssen I, Okely AD, Spence JC, Timmons BW, Sampson M, Tremblay MS. Systematic review of the relationships between physical activity and health indicators in the early years (0-4 years) BMC Public Health. 2017 Nov 20;17(Suppl 5):854. doi: 10.1186/s12889-017-4860-0. https://bmcpublichealth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12889-017-48... 10.1186/s12889-017-4860-0 - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Leppänen MH, Nyström CD, Henriksson P, Pomeroy J, Ruiz JR, Ortega FB, Cadenas-Sánchez C, Löf M. Physical activity intensity, sedentary behavior, body composition and physical fitness in 4-year-old children: results from the ministop trial. Int J Obes (Lond) 2016 Jul;40(7):1126–33. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2016.54.ijo201654 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aubert S, Barnes JD, Abdeta C, Abi Nader P, Adeniyi AF, Aguilar-Farias N, Andrade Tenesaca DS, Bhawra J, Brazo-Sayavera J, Cardon G, Chang CK, Delisle Nyström C, Demetriou Y, Draper CE, Edwards L, Emeljanovas A, Gába A, Galaviz KI, González SA, Herrera-Cuenca M, Huang WY, Ibrahim IA, Jürimäe J, Kämppi K, Katapally TR, Katewongsa P, Katzmarzyk PT, Khan A, Korcz A, Kim YS, Lambert E, Lee EY, Löf M, Loney T, López-Taylor J, Liu Y, Makaza D, Manyanga T, Mileva B, Morrison SA, Mota J, Nyawornota VK, Ocansey R, Reilly JJ, Roman-Viñas B, Silva DA, Saonuam P, Scriven J, Seghers J, Schranz N, Skovgaard T, Smith M, Standage M, Starc G, Stratton G, Subedi N, Takken T, Tammelin T, Tanaka C, Thivel D, Tladi D, Tyler R, Uddin R, Williams A, Wong SHS, Wu C, Zembura P, Tremblay MS. Global matrix 3.0 physical activity report card grades for children and youth: results and analysis from 49 countries. J Phys Act Health. 2018 Nov 1;15(S2):S251–73. doi: 10.1123/jpah.2018-0472. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous