Impact of Abstinence and of Reducing Illicit Drug Use Without Abstinence on Human Immunodeficiency Virus Viral Load
- PMID: 30994900
- PMCID: PMC7319266
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciz299
Impact of Abstinence and of Reducing Illicit Drug Use Without Abstinence on Human Immunodeficiency Virus Viral Load
Abstract
Background: Substance use is common among people living with human immunodeficiency virus (PLWH) and a barrier to achieving viral suppression. Among PLWH who report illicit drug use, we evaluated associations between HIV viral load (VL) and reduced use of illicit opioids, methamphetamine/crystal, cocaine/crack, and marijuana, regardless of whether or not abstinence was achieved.
Methods: This was a longitudinal cohort study of PLWH from 7 HIV clinics or 4 clinical studies. We used joint longitudinal and survival models to examine the impact of decreasing drug use and of abstinence for each drug on viral suppression. We repeated analyses using linear mixed models to examine associations between change in frequency of drug use and VL.
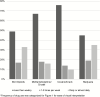
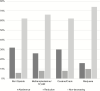
Results: The number of PLWH who were using each drug at baseline ranged from n = 568 (illicit opioids) to n = 4272 (marijuana). Abstinence was associated with higher odds of viral suppression (odds ratio [OR], 1.4-2.2) and lower relative VL (ranging from 21% to 42% by drug) for all 4 drug categories. Reducing frequency of illicit opioid or methamphetamine/crystal use without abstinence was associated with VL suppression (OR, 2.2, 1.6, respectively). Reducing frequency of illicit opioid or methamphetamine/crystal use without abstinence was associated with lower relative VL (47%, 38%, respectively).
Conclusions: Abstinence was associated with viral suppression. In addition, reducing use of illicit opioids or methamphetamine/crystal, even without abstinence, was also associated with viral suppression. Our findings highlight the impact of reducing substance use, even when abstinence is not achieved, and the potential benefits of medications, behavioral interventions, and harm-reduction interventions.
Keywords: abstinence; drug use; heroin; substance use; viral suppression.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


References
-
- Chander G, Himelhoch S, Moore RD. Substance abuse and psychiatric disorders in HIV-positive patients: epidemiology and impact on antiretroviral therapy. Drugs 2006; 66:769–89. - PubMed
-
- Bing EG, Burnam MA, Longshore D, et al. Psychiatric disorders and drug use among human immunodeficiency virus-infected adults in the United States. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2001; 58:721–8. - PubMed
-
- Galvan FH, Bing EG, Fleishman JA, et al. The prevalence of alcohol consumption and heavy drinking among people with HIV in the United States: results from the HIV Cost and Services Utilization Study. J Stud Alcohol 2002; 63:179–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DA030776/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH062294/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA030771/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA032061/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R34 DA035728/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA030762/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA032082/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA032098/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA030778/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA020802/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA032059/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA030793/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA037702/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA030766/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA036935/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027767/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA032100/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH094090/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA032083/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA032057/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA032106/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA030781/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA032110/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA030770/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AA020801/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL126538/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027757/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA030768/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA047045/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA020793/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI094189/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA032080/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA030747/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R24 AI067039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050410/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States

