Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear Promotes Skeletal Muscle Myostatin Expression, Fibrogenic Cell Expansion, and a Decline in Muscle Quality
- PMID: 30995070
- PMCID: PMC6995871
- DOI: 10.1177/0363546519832864
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear Promotes Skeletal Muscle Myostatin Expression, Fibrogenic Cell Expansion, and a Decline in Muscle Quality
Abstract
Background: Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears result in significant quadriceps muscle atrophy that is resistant to recovery despite extensive rehabilitation. Recent work suggests an elevated fibrotic burden in the quadriceps muscle after the injury, which may limit recovery. Elucidating the mechanisms and cell types involved in the progression of fibrosis is critical for developing new treatment strategies.
Purpose: To identify factors contributing to the elevated fibrotic burden found after the injury.
Study design: Descriptive laboratory study.
Methods: After an ACL injury, muscle biopsy specimens were obtained from the injured and noninjured vastus lateralis of young adults (n = 14, mean ± SD: 23 ± 4 years). The expression of myostatin, transforming growth factor β, and other regulatory factors was measured, and immunohistochemical analyses were performed to assess turnover of extracellular matrix components.
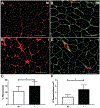
Results: Injured limb skeletal muscle demonstrated elevated myostatin gene ( P < .005) and protein ( P < .0005) expression, which correlated ( R2 = 0.38, P < .05) with fibroblast cell abundance. Immunohistochemical analysis showed that human fibroblasts express the activin type IIB receptor and that isolated primary human muscle-derived fibroblasts increased proliferation after myostatin treatment in vitro ( P < .05). Collagen 1 and fibronectin, primary components of the muscle extracellular matrix, were significantly higher in the injured limb ( P < .05). The abundance of procollagen 1-expressing cells as well as a novel index of collagen remodeling was also elevated in the injured limb ( P < .05).
Conclusion: These findings support a role for myostatin in promoting fibrogenic alterations within skeletal muscle after an ACL injury.
Clinical relevance: The current work shows that the cause of muscle quality decline after ACL injury likely involves elevated myostatin expression, and future studies should explore therapeutic inhibition of myostatin to facilitate improvements in muscle recovery and return to sport.
Keywords: collagen; extracellular matrix; fibroblast; quadriceps.
Figures





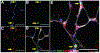


References
-
- Allen DL, Unterman TG. Regulation of myostatin expression and myoblast differentiation by FoxO and SMAD transcription factors. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007;292(1):C188–C199. - PubMed
-
- Angelozzi M, Madama M, Corsica C, et al. Rate of force development as an adjunctive outcome measure for return-to-sport decisions after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2012;42(9):772–780. - PubMed
-
- Ardern CL, Taylor NF, Feller JA, Webster KE. Fifty-five per cent return to competitive sport following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis including aspects of physical functioning and contextual factors. Br J Sports Med. 2014;48(21):1543–1552. - PubMed
-
- Ardern CL, Taylor NF, Feller JA, Webster KE. Return-to-sport outcomes at 2 to 7 years after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40(1):41–48. - PubMed
-
- Ardern CL, Webster KE, Taylor NF, Feller JA. Return to sport following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the state of play. Br J Sports Med. 2011;45(7):596–606. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

