Combined Collagen-Induced Arthritis and Organic Dust-Induced Airway Inflammation to Model Inflammatory Lung Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 30995344
- PMCID: PMC6744331
- DOI: 10.1002/jbmr.3745
Combined Collagen-Induced Arthritis and Organic Dust-Induced Airway Inflammation to Model Inflammatory Lung Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is characterized by extra-articular involvement including lung disease, yet the mechanisms linking the two conditions are poorly understood. The collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) model was combined with the organic dust extract (ODE) airway inflammatory model to assess bone/joint-lung inflammatory outcomes. DBA/1J mice were intranasally treated with saline or ODE daily for 5 weeks. CIA was induced on days 1 and 21. Treatment groups included sham (saline injection/saline inhalation), CIA (CIA/saline), ODE (saline/ODE), and CIA + ODE (CIA/ODE). Arthritis inflammatory scores, bones, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, lung tissues, and serum were assessed. In DBA/1J male mice, arthritis was increased in CIA + ODE > CIA > ODE versus sham. Micro-computed tomography (µCT) demonstrated that loss of BMD and volume and deterioration of bone microarchitecture was greatest in CIA + ODE. However, ODE-induced airway neutrophil influx and inflammatory cytokine/chemokine levels in lavage fluids were increased in ODE > CIA + ODE versus sham. Activated lung CD11c+ CD11b+ macrophages were increased in ODE > CIA + ODE > CIA pattern, whereas lung hyaluronan, fibronectin, and amphiregulin levels were greatest in CIA + ODE. Serum autoantibody and inflammatory marker concentrations varied among experimental groups. Compared with male mice, female mice showed less articular and pulmonary disease. The interaction of inhalation-induced airway inflammation and arthritis induction resulted in compartmentalized responses with the greatest degree of arthritis and bone loss in male mice with combined exposures. Data also support suppression of the lung inflammatory response, but increases in extracellular matrix protein deposition/interstitial disease in the setting of arthritis. This coexposure model could be exploited to better understand and treat RA-lung disease. © 2019 American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
Keywords: AUTOIMMUNITY; COEXPOSURE; INFLAMMATION; INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE; RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS.
© 2019 American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
Figures

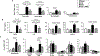
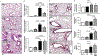

References
-
- Erickson AR, Canella AC, Mikuls TR. 2017. Clinical features of rheumatoid arthritis In: Budd RC, Gabriel SB, McInnes IB, O’Dell JR (ed) Kelley & Firestein’s Textbook of Rheumatology, II ed, Elsevier, Philadelphia, pp. 1167-1167–1186.
-
- England BR, Sayles H, Michaud K, Caplan L, Davis LA, Cannon GW, Sauer BC, Solow EB, Reimold AM, Kerr GS, Schwab P, Baker JF, Mikuls TR 2016. Cause-Specific Mortality in Male US Veterans With Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 68:36–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

