Single-Cell RNA-Sequencing-Based CRISPRi Screening Resolves Molecular Drivers of Early Human Endoderm Development
- PMID: 30995470
- PMCID: PMC6525305
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.03.076
Single-Cell RNA-Sequencing-Based CRISPRi Screening Resolves Molecular Drivers of Early Human Endoderm Development
Abstract
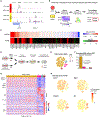
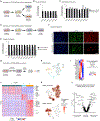
Studies in vertebrates have outlined conserved molecular control of definitive endoderm (END) development. However, recent work also shows that key molecular aspects of human END regulation differ even from rodents. Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells (ESCs) to END offers a tractable system to study the molecular basis of normal and defective human-specific END development. Here, we interrogated dynamics in chromatin accessibility during differentiation of ESCs to END, predicting DNA-binding proteins that may drive this cell fate transition. We then combined single-cell RNA-seq with parallel CRISPR perturbations to comprehensively define the loss-of-function phenotype of those factors in END development. Following a few candidates, we revealed distinct impairments in the differentiation trajectories for mediators of TGFβ signaling and expose a role for the FOXA2 transcription factor in priming human END competence for human foregut and hepatic END specification. Together, this single-cell functional genomics study provides high-resolution insight on human END development.
Keywords: CRISPRi; chromatin accessibility; dCas9-KRAB; endoderm; hepatic endoderm; human development; perturbation screen; pluripotent stem cells; single-cell RNA-seq; stem cell differentiation.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Alexander J, and Stainier DY (1999). A molecular pathway leading to endoderm formation in zebrafish. Curr. Biol 9, 1147–1157. - PubMed
-
- Allison TF, Smith AJH, Anastassiadis K, Sloane-Stanley J, Biga V, Stavish D, Hackland J, Sabri S, Langerman J, Jones M, et al. (2018). Identification and single-cell functional characterization of an endodermally biased pluripotent substate in human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cell Reports 10, 1895–1907. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ang SL, and Rossant J (1994). HNF-3 beta is essential for node and noto-chord formation in mouse development. Cell 78, 561–574. - PubMed
-
- Avery S, Zafarana G, Gokhale PJ, and Andrews PW (2010). The role of SMAD4 in human embryonic stem cell self-renewal and stem cell fate. Stem Cells 28, 863–873. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

