Shared and Distinct Functions of Type I and Type III Interferons
- PMID: 30995506
- PMCID: PMC6839410
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.03.025
Shared and Distinct Functions of Type I and Type III Interferons
Abstract
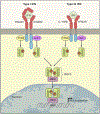
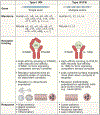
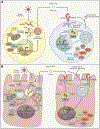
Type I interferons (IFNs) (IFN-α, IFN-β) and type III IFNs (IFN-λ) share many properties, including induction by viral infection, activation of shared signaling pathways, and transcriptional programs. However, recent discoveries have revealed context-specific functional differences. Here, we provide a comprehensive review of type I and type III IFN activities, highlighting shared and distinct features from molecular mechanisms through physiological responses. Beyond discussing canonical antiviral functions, we consider the adaptive immune priming, anti-tumor, and autoimmune functions of IFNs. We discuss a model wherein type III IFNs serve as a front-line defense that controls infection at epithelial barriers while minimizing damaging inflammatory responses, reserving the more potent type I IFN response for when local responses are insufficient. In this context, we discuss current therapeutic applications targeting these cytokine pathways and highlight gaps in understanding of the biology of type I and type III IFNs in health and disease.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
M.S.D. is a consultant for Inbios and Atreca and is on the Scientific Advisory Board of Moderna.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

