Insights into the Molecular Mechanisms of Eg5 Inhibition by (+)-Morelloflavone
- PMID: 30995725
- PMCID: PMC6630617
- DOI: 10.3390/ph12020058
Insights into the Molecular Mechanisms of Eg5 Inhibition by (+)-Morelloflavone
Abstract
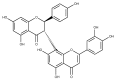
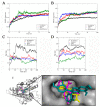
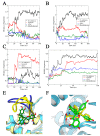
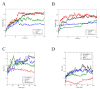
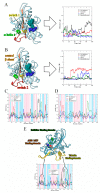
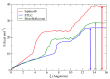
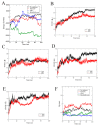
(+)-Morelloflavone (MF) is an antitumor biflavonoid that is found in the Garcinia species. Recently, we reported MF as a novel inhibitor of ATPase and microtubules-gliding activities of the kinesin spindle protein (Eg5) in vitro. Herein, we provide dynamical insights into the inhibitory mechanisms of MF against Eg5, which involves binding of the inhibitor to the loop5/α2/α3 allosteric pocket. Molecular dynamics simulations were carried out for 100 ns on eight complexes: Eg5-Adenosine diphosphate (Eg5-ADP), Eg5-ADP-S-trityl-l-cysteine (Eg5-ADP-STLC), Eg5-ADP-ispinesib, Eg5-ADP-MF, Eg5-Adenosine triphosphate (Eg5-ATP), Eg5-ATP-STLC, Eg5-ATP-ispinesib, and Eg5-ATP-MF complexes. Structural and energetic analyses were done using Umbrella sampling, Molecular Mechanics Poisson-Boltzmann Surface Area (MM/PBSA) method, GROMACS analysis toolkit, and virtual molecular dynamics (VMD) utilities. The results were compared with those of the known Eg5 inhibitors; ispinesib, and STLC. Our data strongly support a stable Eg5-MF complex, with significantly low binding energy and reduced flexibility of Eg5 in some regions, including loop5 and switch I. Furthermore, the loop5 Trp127 was trapped in a downward position to keep the allosteric pocket of Eg5 in the so-called "closed conformation", comparable to observations for STLC. Altered structural conformations were also visible within various regions of Eg5, including switch I, switch II, α2/α3 helices, and the tubulin-binding region, indicating that MF might induce modifications in the Eg5 structure to compromise its ATP/ADP binding and conversion process as well as its interaction with microtubules. The described mechanisms are crucial for understanding Eg5 inhibition by MF.
Keywords: (+)-morelloflavone; biflavonoid; inhibitors; kinesin Eg5; molecular dynamics; molecular interaction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

