Oral Vaccination with Replication-Competent Adenovirus in Mice Reveals Dissemination of the Viral Vaccine beyond the Gastrointestinal Tract
- PMID: 30996103
- PMCID: PMC6580940
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00237-19
Oral Vaccination with Replication-Competent Adenovirus in Mice Reveals Dissemination of the Viral Vaccine beyond the Gastrointestinal Tract
Abstract
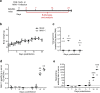
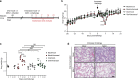
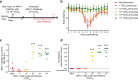
Since the 1970s, replication-competent human adenoviruses 4 and 7 have been used as oral vaccines to protect U.S. soldiers against the severe respiratory diseases caused by these viruses. These vaccines are thought to establish a digestive tract infection conferring protection against respiratory challenge through antibodies. The success of these vaccines makes replication-competent adenoviruses attractive candidates for use as oral vaccine vectors. However, the inability of human adenoviruses to replicate efficiently in laboratory animals has hampered the study of such vectors. Here, we used mouse adenovirus type 1 (MAV-1) in mice to study oral replication-competent adenovirus-based vaccines. We show that MAV-1 oral administration provides protection that recapitulates the protection against homologous respiratory challenge observed with adenovirus 4 and 7 vaccines. Moreover, live oral MAV-1 vaccine better protected against a respiratory challenge than inactivated vaccines. This protection was linked not only with the presence of MAV-1-specific antibodies but also with a better recruitment of effector CD8 T cells. However, unexpectedly, we found that such oral replication-competent vaccine systemically spread all over the body. Our results therefore support the use of MAV-1 to study replication-competent oral adenovirus-based vaccines but also highlight the fact that those vaccines can disseminate widely in the body.IMPORTANCE Replication-competent adenoviruses appear to be promising vectors for the development of oral vaccines in humans. However, the study and development of these vaccines suffer from the lack of any reliable animal model. In this study, mouse adenovirus type 1 was used to develop a small-animal model for oral replication-competent adenovirus vaccines. While this model reproduced in mice what is observed with human adenovirus oral vaccines, it also highlighted that oral immunization with such a replication-competent vaccine is associated with the systemic spread of the virus. This study is therefore of major importance for the future development of such vaccine platforms and their use in large human populations.
Keywords: adenovirus; mouse model; oral vaccination.
Copyright © 2019 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures






Similar articles
-
A Single Oral Immunization with a Replication-Competent Adenovirus-Vectored Vaccine Protects Mice from Influenza Respiratory Infection.J Virol. 2023 Jul 27;97(7):e0013523. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00135-23. Epub 2023 Jun 20. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 37338377 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Efficacy of Rhesus Adenovirus COVID-19 Vaccines against Mouse-Adapted SARS-CoV-2.J Virol. 2021 Nov 9;95(23):e0097421. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00974-21. Epub 2021 Sep 15. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34523968 Free PMC article.
-
A Single Oral Immunization with Replication-Competent Adenovirus-Vectored Vaccine Induces a Neutralizing Antibody Response in Mice against Canine Distemper Virus.Viruses. 2022 Aug 23;14(9):1847. doi: 10.3390/v14091847. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36146652 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccination against acute respiratory virus infections and measles in man.Immunobiology. 1992 Feb;184(2-3):180-92. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80474-2. Immunobiology. 1992. PMID: 1587542 Review.
-
[Novel vaccines against M. tuberculosis].Kekkaku. 2006 Dec;81(12):745-51. Kekkaku. 2006. PMID: 17240920 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
COVID-19: should oral vaccination strategies be given more consideration?Ther Adv Vaccines Immunother. 2020 Jul 27;8:2515135520946503. doi: 10.1177/2515135520946503. eCollection 2020. Ther Adv Vaccines Immunother. 2020. PMID: 32778854 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Circulating Adaptive Immune Cells Expressing the Gut Homing Marker α4β7 Integrin Are Decreased in COVID-19.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 20;12:639329. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.639329. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33959123 Free PMC article.
-
Using crystallography tools to improve vaccine formulations.IUCrJ. 2021 Nov 25;9(Pt 1):11-20. doi: 10.1107/S205225252101071X. eCollection 2022 Jan 1. IUCrJ. 2021. PMID: 35059205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral subunit SARS-CoV-2 vaccine induces systemic neutralizing IgG, IgA and cellular immune responses and can boost neutralizing antibody responses primed by an injected vaccine.Vaccine. 2022 Feb 16;40(8):1098-1107. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2022.01.025. Epub 2022 Jan 19. Vaccine. 2022. PMID: 35078662 Free PMC article.
-
The RGD-binding integrins αvβ6 and αvβ8 are receptors for mouse adenovirus-1 and -3 infection.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Dec 15;17(12):e1010083. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010083. eCollection 2021 Dec. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 34910784 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

