Discovery of Small-Molecule Inhibitors Targeting the E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Activity of the Herpes Simplex Virus 1 ICP0 Protein Using an In Vitro High-Throughput Screening Assay
- PMID: 30996104
- PMCID: PMC6580980
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00619-19
Discovery of Small-Molecule Inhibitors Targeting the E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Activity of the Herpes Simplex Virus 1 ICP0 Protein Using an In Vitro High-Throughput Screening Assay
Abstract
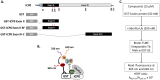
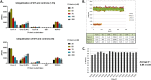
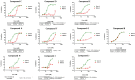
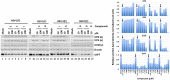
Herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) has infected more than 80% of the population. Reactivation of the virus causes diseases ranging in severity from benign cold sores to fatal encephalitis. Current treatments involve viral DNA replication inhibitors, but the emergence of drug-resistant mutants is observed frequently, highlighting the need for novel antiviral therapies. Infected cell protein 0 (ICP0) of HSV-1 is encoded by an immediate early gene and plays a fundamental role during infection, because it enables viral gene expression and blocks antiviral responses. One mechanism by which ICP0 functions is through an E3 ubiquitin ligase activity that induces the degradation of targeted proteins. A ΔICP0 virus or mutants with deficiencies in E3 ligase activity cannot counteract beta interferon (IFN-β)-induced restriction of viral infection, are highly immunogenic, are avirulent, and fail to spread. Thus, small molecules interfering with essential and conserved ICP0 functions are expected to compromise HSV-1 infection. We have developed a high-throughput screening assay, based on the autoubiquitination properties of ICP0, to identify small-molecule inhibitors of ICP0 E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. Through a pilot screening procedure, we identified nine compounds that displayed dose-dependent inhibitory effects on ICP0 but not on Mdm2, a control E3 ubiquitin ligase. Following validation, one compound displayed ICP0-dependent inhibition of HSV-1 infection. This compound appeared to bind ICP0 in a cellular thermal shift assay, it blocked ICP0 self-elimination, and it blocked wild-type but not ICP0-null virus gene expression. This scaffold displays specificity and could be used to develop optimized ICP0 E3 ligase inhibitors.IMPORTANCE Since acyclovir and its derivatives were launched for herpesviruses control almost four decades ago, the search for novel antivirals has waned. However, as human life expectancy has increased, so has the number of immunocompromised individuals who receive prolonged treatment for HSV recurrences. This has led to an increase in unresponsive patients due to acquired viral drug resistance. Thus, novel treatments need to be explored. Here we explored the HSV-1 ICP0 E3 ligase as a potential antiviral target because (i) ICP0 is expressed before virus replication, (ii) it is essential for infection in vivo, (iii) it is required for efficient reactivation of the virus from latency, (iv) inhibition of its E3 ligase activity would sustain host immune responses, and (v) it is shared by other herpesviruses. We report a compound that inhibits HSV-1 infection in an ICP0-dependent manner by inhibiting ICP0 E3 ligase activity.
Keywords: E3 ubiquitin ligase; HSV; ICP0; high-throughput screening assay; small-molecule inhibitors.
Copyright © 2019 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of Elements Regulating the Nuclear-to-Cytoplasmic Translocation of ICP0 in Late Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Infection.J Virol. 2018 Jan 2;92(2):e01673-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01673-17. Print 2018 Jan 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29093084 Free PMC article.
-
A Tale of Two PMLs: Elements Regulating a Differential Substrate Recognition by the ICP0 E3 Ubiquitin Ligase of Herpes Simplex Virus 1.J Virol. 2016 Nov 14;90(23):10875-10885. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01636-16. Print 2016 Dec 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27681131 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between the cellular E3 ubiquitin ligase SIAH-1 and the viral immediate-early protein ICP0 enables efficient replication of Herpes Simplex Virus type 2 in vivo.PLoS One. 2018 Aug 6;13(8):e0201880. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0201880. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30080903 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of alphaherpesvirus infections by the ICP0 family of proteins.J Gen Virol. 2013 Mar;94(Pt 3):465-481. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.048900-0. Epub 2012 Dec 12. J Gen Virol. 2013. PMID: 23239572 Review.
-
The HSV-1 ubiquitin ligase ICP0: Modifying the cellular proteome to promote infection.Virus Res. 2020 Aug;285:198015. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198015. Epub 2020 May 13. Virus Res. 2020. PMID: 32416261 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
HSV-1 ICP0 Dimer Domain Adopts a Novel β-barrel Fold.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 16:2024.01.16.575752. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.16.575752. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Proteins. 2024 Jul;92(7):830-841. doi: 10.1002/prot.26673. PMID: 38293217 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
A Systematic Review of Second-Line Treatments in Antiviral Resistant Strains of HSV-1, HSV-2, and VZV.Cureus. 2023 Mar 9;15(3):e35958. doi: 10.7759/cureus.35958. eCollection 2023 Mar. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37041924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of E3 ubiquitin ligases in bone homeostasis and related diseases.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023 Oct;13(10):3963-3987. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.06.016. Epub 2023 Jul 6. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023. PMID: 37799379 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HSV-1 ICP0 dimer domain adopts a novel β-barrel fold.Proteins. 2024 Jul;92(7):830-841. doi: 10.1002/prot.26673. Epub 2024 Feb 19. Proteins. 2024. PMID: 38372168 Free PMC article.
-
"Non-Essential" Proteins of HSV-1 with Essential Roles In Vivo: A Comprehensive Review.Viruses. 2020 Dec 23;13(1):17. doi: 10.3390/v13010017. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 33374862 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Roizman B, Knipe DM, Whitley RJ. 2013. Herpes simplex viruses, p 1823–1897. In Knipe DM, Howley PM, Cohen JI, Griffin DE, Lamb RA, Martin MA, Roizman B (ed), Fields virology, 6th ed Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

