Esophageal pressure balloon and transpulmonary pressure monitoring in airway pressure release ventilation: a different approach
- PMID: 30996644
- PMCID: PMC6422107
- DOI: 10.29390/cjrt-2018-010
Esophageal pressure balloon and transpulmonary pressure monitoring in airway pressure release ventilation: a different approach
Abstract
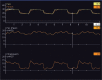
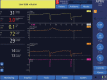
This is a case of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome managed using esophageal balloon catheter to adjust inspiratory pressure and positive end expiratory pressure according to the inspiratory and expiratory transpulmonary pressures. There are no studies that examine the transpulmonary pressures in airway pressure release ventilation (APRV). We aimed to test the feasibility of using the esophageal balloon in the nonconventional mode of APRV. All pressures were observed when switching the mode from a pressure-controlled mode to APRV using the same inspiratory pressure and using various incremental release times (TLow)to calculate the expiratory transpulmonary pressure. At all TLow levels the transpulmonary pressure at end exhalation was in the negative value indicating alveolar collapse. A larger study is needed to confirm our findings and to help guide setting APRV.
Keywords: APRV; PEEP; esophageal balloon; transpulmonary pressure.
Figures



References
-
- Akoumianaki E, Maggiore SM, Valenza F, Bellani G, Jubran A, Loring SH, et al. . The application of esophageal pressure measurement in patients with respiratory failure. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2014; 189(5): 520–31. - PubMed
-
- Slutsky AS, Ranieri VM, Ventilator-induced lung injury. N Engl J Med 2013; 369(22): 2126–36 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
