Nivolumab and immune-mediated colitis
- PMID: 30997054
- PMCID: PMC6452469
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.2027
Nivolumab and immune-mediated colitis
Abstract
Nivolumab is associated with a number of immune-regulated adverse events, including immune-mediated colitis and may present following the discontinuation of treatment. Current guidance suggests lower doses of methylprednisolone; however, we described faster resolution of the patient's symptoms compared to previous reported cases, using higher dosing, thereby minimizing hospitalization.
Keywords: Nivolumab; PD‐1 receptor; immune‐mediated colitis; immune‐regulated adverse events.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no competing interests.
Figures
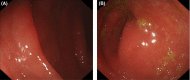
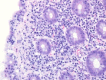
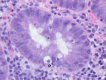
References
-
- Wolchok JD. PD‐1 blockers. Cell. 2015;162(5):937. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez RS, Salaria SN, Bohannon CD, Huber AR, Feely MM, Shi C. PD‐1 inhibitor gastroenterocolitis: case series and appraisal of 'immunomodulatory gastroenterocolitis'. Histopathology. 2017;70(4):558‐567. - PubMed
-
- Eigentler TK, Hassel JC, Berking C, et al. Diagnosis, monitoring and management of immune‐related adverse drug reactions of anti‐PD‐1 antibody therapy. Cancer Treat Rev. 2016;45:7‐18. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

