Assessing oil accumulation in the oleaginous yeast Cystobasidium oligophagum JRC1 using dairy waste cheese whey as a substrate
- PMID: 30997310
- PMCID: PMC6458212
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-019-1701-0
Assessing oil accumulation in the oleaginous yeast Cystobasidium oligophagum JRC1 using dairy waste cheese whey as a substrate
Abstract
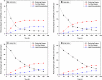
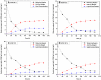
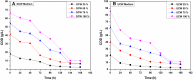
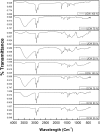
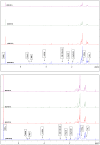
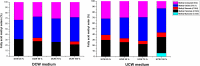
This study assesses the potential for the lipid production by the oleaginous yeast Cystobasidium oligophagum JRC1 using dairy industry waste cheese whey as a substrate. Cheese whey was used either untreated (UCW) or deproteinized (DCW) at different concentrations (25-100%) to serve as the carbon and energy source. Both UCW and DCW supported high biomass and lipid productivities. The biomass productivity of 0.076 ± 0.0004 and 0.124 ± 0.0021 g/L h, lipid productivity of 0.0335 ± 0.0004 and 0.0272 ± 0.0008 g/L h, and the lipid content of 44.12 ± 0.84 and 21.79 ± 1.00% were achieved for 100% DCW and UCW, respectively. The soluble chemical oxygen demand (sCOD) removal rate was 8.049 ± 0.198 and 10.61 ± 0.0165 g/L day (84.91 ± 0.155 and 86.82 ± 0.067% removal) for 100% DCW and UCW, respectively. Fatty acid methyl ester (FAME) composition obtained using GC-FID studies revealed the presence of C16 and C18 fatty acid in the lipid extract and the biodiesel properties were found to be in accordance with ASTM and EN standards. The study presents a method for the valorization of cheese whey waste into a feasible feedstock for biodiesel.
Keywords: Biodiesel; Cheese whey; Cystobasidium oligophagum; Deproteinized cheese whey; Oleaginous yeast; Rhodotorula.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethical standardsThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest in the publication.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Isolation, identification and characterization of Cystobasidium oligophagum JRC1: A cellulase and lipase producing oleaginous yeast.Bioresour Technol. 2017 Jan;223:250-258. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2016.10.039. Epub 2016 Oct 15. Bioresour Technol. 2017. PMID: 27969576
-
A sustainable use of Ricotta Cheese Whey for microbial biodiesel production.Sci Total Environ. 2017 Apr 15;584-585:554-560. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.01.068. Epub 2017 Feb 3. Sci Total Environ. 2017. PMID: 28169024
-
Mutants of Yarrowia lipolytica NCIM 3589 grown on waste cooking oil as a biofactory for biodiesel production.Microb Cell Fact. 2017 Oct 24;16(1):176. doi: 10.1186/s12934-017-0790-x. Microb Cell Fact. 2017. PMID: 29065878 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous lipid production for biodiesel feedstock and decontamination of sago processing wastewater using Candida tropicalis ASY2.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2020 Mar 5;13:35. doi: 10.1186/s13068-020-01676-1. eCollection 2020. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2020. PMID: 32158499 Free PMC article.
-
Dairy By-Products: A Review on the Valorization of Whey and Second Cheese Whey.Foods. 2021 May 12;10(5):1067. doi: 10.3390/foods10051067. Foods. 2021. PMID: 34066033 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Whole conversion of agro-industrial wastes rich in galactose-based carbohydrates into lipid using oleaginous yeast Aureobasidium namibiae.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2021 Sep 15;14(1):181. doi: 10.1186/s13068-021-02031-8. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2021. PMID: 34526122 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Cell Protein and Ethanol Production of a Newly Isolated Kluyveromyces marxianus Strain through Cheese Whey Valorization.Foods. 2024 Jun 16;13(12):1892. doi: 10.3390/foods13121892. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38928833 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous production of biofuel from agricultural wastes and bioremediation of the waste substrates: A review.Curr Res Microb Sci. 2024 Nov 15;7:100305. doi: 10.1016/j.crmicr.2024.100305. eCollection 2024. Curr Res Microb Sci. 2024. PMID: 39620096 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Annamalai N, Sivakumar N, Oleskowicz-Popiel P. Enhanced production of microbial lipids from waste office paper by the oleaginous yeast Cryptococcus curvatus. Fuel. 2018;217:420–426. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.12.108. - DOI
-
- AOAC Method Ce 1-62 (2005) Fatty acid composition by gas chromatography. In: Firestone D (ed) Official methods of analysis of AOAC, 18th edn, AOAC International, Gaithersburg, Maryland.
-
- APHA . Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 21. Washington: American Public Health Association; 2005.
-
- Arous F, Frikha F, Triantaphyllidou IE, et al. Potential utilization of agro-industrial wastewaters for lipid production by the oleaginous yeast Debaryomyces etchellsii. J Clean Prod. 2016;133:899–909. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.06.040. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

