Health Education Training Embedded in a Microfinance Platform Associated with Safer Sexual Behavior in Haitian Women
- PMID: 30997651
- PMCID: PMC7979276
- DOI: 10.1007/s10461-019-02511-x
Health Education Training Embedded in a Microfinance Platform Associated with Safer Sexual Behavior in Haitian Women
Abstract
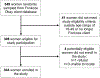
Sexual health education interventions have generally yielded modest impact, but may be more successful when integrated into programs designed to alleviate poverty and empower women. Between December 2017 and February 2018, we interviewed 304 Haitian female microfinance clients, 75 of whom had received health education training delivered within their regular meetings. Participants reported six key sexual health outcomes. We used log-binomial models to estimate the association between health education training and each outcome, and tested for interaction by age and literacy status. Women with health education training reported more condom use with unfaithful partners [PR (95% CI) 1.78 (1.04, 3.02)], more HIV testing [PR (95% CI) 1.56 (1.28, 1.90)], and fewer STI symptoms [PR (95% CI) 0.37 (0.19, 0.73)], compared to women with no training. Some of the associations were stronger among older women [e.g. HIV testing: PR (95% CI) 2.09 (1.49, 2.82)] and illiterate women [e.g. condom use: PR (95% CI) 3.46 (1.05, 11.38)]. These findings add to the growing body of evidence demonstrating the potential to use microfinance programs as platforms for health education delivery, and provide the first evidence for the association in Haiti.
Keywords: HIV; Haiti; Microfinance; STI; Sexual behavior.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of a microfinance program on HIV risk behavior among Haitian women.AIDS Behav. 2011 Jul;15(5):911-8. doi: 10.1007/s10461-010-9860-3. AIDS Behav. 2011. PMID: 21153762
-
Consistent condom use among highly effective contraceptive users in an HIV-endemic area in rural Kenya.PLoS One. 2019 May 6;14(5):e0216208. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0216208. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31059524 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship of psychosocial factors to HIV risk among Haitian women.AIDS Educ Prev. 2000 Feb;12(1):79-92. AIDS Educ Prev. 2000. PMID: 10749388
-
Interventions to reduce sexual risk for the human immunodeficiency virus in adolescents, 1985-2000: a research synthesis.Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2003 Apr;157(4):381-8. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.157.4.381. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2003. PMID: 12695235 Review.
-
Microfinance Interventions and HIV Treatment Outcomes: A Synthesizing Conceptual Framework and Systematic Review.AIDS Behav. 2019 Sep;23(9):2238-2252. doi: 10.1007/s10461-019-02443-6. AIDS Behav. 2019. PMID: 30805757 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Relationship Between Household Microfinance Group Participation and Vaccine Adherence Among Children in Rural Western Kenya.Matern Child Health J. 2021 Nov;25(11):1725-1734. doi: 10.1007/s10995-021-03217-0. Epub 2021 Aug 18. Matern Child Health J. 2021. PMID: 34409522 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between hurricane exposure, food insecurity, and microfinance; a cross-sectional study in Haiti.World Dev. 2021 Sep;145:105530. doi: 10.1016/j.worlddev.2021.105530. Epub 2021 May 8. World Dev. 2021. PMID: 34177044 Free PMC article.
-
U.S. transgender women's preferences for microeconomic interventions to address structural determinants of HIV vulnerability: a qualitative assessment.BMC Public Health. 2021 Jul 14;21(1):1394. doi: 10.1186/s12889-021-11471-8. BMC Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34261464 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS. The Gap Report. Geneva: UNAIDS; 2014.
-
- UNAIDS. Country Fact Sheet: Haiti: 2017. [Available from: http://www.unaids.org/en/regionscountries/countries/haiti.
-
- Republique D’Haïti Ministere de la Sante Publique et de la Population. Declaration d’engagement sur le VIH/sida: Rapport de situation nationale, Haïti. 2016.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

