Metformin and second- or third-generation sulphonylurea combination therapy for adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 30998259
- PMCID: PMC6472662
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012368.pub2
Metformin and second- or third-generation sulphonylurea combination therapy for adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Background: The number of people with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is increasing worldwide. The combination of metformin and sulphonylurea (M+S) is a widely used treatment. Whether M+S shows better or worse effects in comparison with other antidiabetic medications for people with T2DM is still controversial.
Objectives: To assess the effects of metformin and sulphonylurea (second- or third-generation) combination therapy for adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Search methods: We updated the search of a recent systematic review from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ). The updated search included CENTRAL, MEDLINE, Embase, ClinicalTrials.gov and WHO ICTRP. The date of the last search was March 2018. We searched manufacturers' websites and reference lists of included trials, systematic reviews, meta-analyses and health technology assessment reports. We asked investigators of the included trials for information about additional trials.
Selection criteria: We included randomised controlled trials (RCTs) randomising participants 18 years old or more with T2DM to M+S compared with metformin plus another glucose-lowering intervention or metformin monotherapy with a treatment duration of 52 weeks or more.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors read all abstracts and full-text articles and records, assessed risk of bias and extracted outcome data independently. We used a random-effects model to perform meta-analysis, and calculated risk ratios (RRs) for dichotomous outcomes and mean differences (MDs) for continuous outcomes, using 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for effect estimates. We assessed the certainty of the evidence using the GRADE instrument.
Main results: We included 32 RCTs randomising 28,746 people. Treatment duration ranged between one to four years. We judged none of these trials as low risk of bias for all 'Risk of bias' domains. Most important events per person were all-cause and cardiovascular mortality, serious adverse events (SAE), non-fatal stroke (NFS), non-fatal myocardial infarction (MI) and microvascular complications. Most important comparisons were as follows:Five trials compared M+S (N = 1194) with metformin plus a glucagon-like peptide 1 analogue (N = 1675): all-cause mortality was 11/1057 (1%) versus 11/1537 (0.7%), risk ratio (RR) 1.15 (95% confidence interval (CI) 0.49 to 2.67); 3 trials; 2594 participants; low-certainty evidence; cardiovascular mortality 1/307 (0.3%) versus 1/302 (0.3%), low-certainty evidence; serious adverse events (SAE) 128/1057 (12.1%) versus 194/1537 (12.6%), RR 0.90 (95% CI 0.73 to 1.11); 3 trials; 2594 participants; very low-certainty evidence; non-fatal myocardial infarction (MI) 2/549 (0.4%) versus 6/1026 (0.6%), RR 0.57 (95% CI 0.12 to 2.82); 2 trials; 1575 participants; very low-certainty evidence.Nine trials compared M+S (N = 5414) with metformin plus a dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 inhibitor (N = 6346): all-cause mortality was 33/5387 (0.6%) versus 26/6307 (0.4%), RR 1.32 (95% CI 0.76 to 2.28); 9 trials; 11,694 participants; low-certainty evidence; cardiovascular mortality 11/2989 (0.4%) versus 9/3885 (0.2%), RR 1.54 (95% CI 0.63 to 3.79); 6 trials; 6874 participants; low-certainty evidence; SAE 735/5387 (13.6%) versus 779/6307 (12.4%), RR 1.07 (95% CI 0.97 to 1.18); 9 trials; 11,694 participants; very low-certainty evidence; NFS 14/2098 (0.7%) versus 8/2995 (0.3%), RR 2.21 (95% CI 0.74 to 6.58); 4 trials; 5093 participants; very low-certainty evidence; non-fatal MI 15/2989 (0.5%) versus 13/3885 (0.3%), RR 1.45 (95% CI 0.69 to 3.07); 6 trials; 6874 participants; very low-certainty evidence; one trial in 64 participants reported no microvascular complications were observed (very low-certainty evidence).Eleven trials compared M+S (N = 3626) with metformin plus a thiazolidinedione (N = 3685): all-cause mortality was 123/3300 (3.7%) versus 114/3354 (3.4%), RR 1.09 (95% CI 0.85 to 1.40); 6 trials; 6654 participants; low-certainty evidence; cardiovascular mortality 37/2946 (1.3%) versus 41/2994 (1.4%), RR 0.78 (95% CI 0.36 to 1.67); 4 trials; 5940 participants; low-certainty evidence; SAE 666/3300 (20.2%) versus 671/3354 (20%), RR 1.01 (95% CI 0.93 to 1.11); 6 trials; 6654 participants; very low-certainty evidence; NFS 20/1540 (1.3%) versus 16/1583 (1%), RR 1.29 (95% CI 0.67 to 2.47); P = 0.45; 2 trials; 3123 participants; very low-certainty evidence; non-fatal MI 25/1841 (1.4%) versus 21/1877 (1.1%), RR 1.21 (95% CI 0.68 to 2.14); P = 0.51; 3 trials; 3718 participants; very low-certainty evidence; three trials (3123 participants) reported no microvascular complications (very low-certainty evidence).Three trials compared M+S (N = 462) with metformin plus a glinide (N = 476): one person died in each intervention group (3 trials; 874 participants; low-certainty evidence); no cardiovascular mortality (2 trials; 446 participants; low-certainty evidence); SAE 34/424 (8%) versus 27/450 (6%), RR 1.68 (95% CI 0.54 to 5.21); P = 0.37; 3 trials; 874 participants; low-certainty evidence; no NFS (1 trial; 233 participants; very low-certainty evidence); non-fatal MI 2/215 (0.9%) participants in the M+S group; 2 trials; 446 participants; low-certainty evidence; no microvascular complications (1 trial; 233 participants; low-certainty evidence).Four trials compared M+S (N = 2109) with metformin plus a sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor (N = 3032): all-cause mortality was 13/2107 (0.6%) versus 19/3027 (0.6%), RR 0.96 (95% CI 0.44 to 2.09); 4 trials; 5134 participants; very low-certainty evidence; cardiovascular mortality 4/1327 (0.3%) versus 6/2262 (0.3%), RR 1.22 (95% CI 0.33 to 4.41); 3 trials; 3589 participants; very low-certainty evidence; SAE 315/2107 (15.5%) versus 375/3027 (12.4%), RR 1.02 (95% CI 0.76 to 1.37); 4 trials; 5134 participants; very low-certainty evidence; NFS 3/919 (0.3%) versus 7/1856 (0.4%), RR 0.87 (95% CI 0.22 to 3.34); 2 trials; 2775 participants; very low-certainty evidence; non-fatal MI 7/890 (0.8%) versus 8/1374 (0.6%), RR 1.43 (95% CI 0.49 to 4.18; 2 trials); 2264 participants; very low-certainty evidence; amputation of lower extremity 1/437 (0.2%) versus 1/888 (0.1%); very low-certainty evidence.Trials reported more hypoglycaemic episodes with M+S combination compared to all other metformin-antidiabetic agent combinations. Results for M+S versus metformin monotherapy were inconclusive. There were no RCTs comparing M+S with metformin plus insulin. We identified nine ongoing trials and two trials are awaiting assessment. Together these trials will include approximately 16,631 participants.
Authors' conclusions: There is inconclusive evidence whether M+S combination therapy compared with metformin plus another glucose-lowering intervention results in benefit or harm for most patient-important outcomes (mortality, SAEs, macrovascular and microvascular complications) with the exception of hypoglycaemia (more harm for M+S combination). No RCT reported on health-related quality of life.
Conflict of interest statement
KM: had an inadvertent conflict of interest because he had owned a small number of shares with Novo Nordisk A/S before registering the title. Without prompting KM amended the situation by selling the shares, so he no longer has a direct financial benefit as first author. Cochrane Metabolic and Endocrine Disorders contacted the Cochrane Funding Arbiter for guidance, who agreed to allow the review to proceed with KM as a first author, providing that this issue was clearly explained in the declarations of interest. KM received a scholarship from Michaelsen Fonden.
PK: equities in Novo Nordisk A/S.
LK: none known.
SM: Advisory Boards: Novartis Pharma, Novo Nordisk, Merck Sharp & Dome, Sanofi‐Aventis, AstraZeneca, Johnson & Johnson, Boehringer‐Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Intarcia Therapeutics, Bristol‐Meyer Squibb. Fee for lectures: Novo Nordisk, Merck, Sharp & Dome, Astra‐Zeneca, Sanofi‐Aventis, Novartis Pharma, Eli Lilly, Bristol‐Meyer Squibb, Boeringer‐Ingelheim. Grants for research: Novo Nordisk.
FG: none known.
MIM: none known.
BR: none known.
BH: none known.
Figures
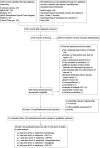

Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Ahrén 2014 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Ahrén B, Johnson SL, Stewart M, Cirkel DT, Yang F, Perry C, et al. HARMONY 3: 104‐week randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐ and active‐controlled trial assessing the efficacy and safety of albiglutide compared with placebo, sitagliptin, and glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes taking metformin. Diabetes Care 2014;37(8):2141‐8. [DOI: 10.2337/dc14-0024] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ahrén B, Stewart M, Cirkel D, Yang F, Perry C, Johnson S. HARMONY 3: 104 week (wk) efficacy of albiglutide (albi) compared to sitagliptin (sita) and glimepiride (SU) in patients (pts) with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) on metformin (met). 73rd Scientific Sessions. American Diabetes Assosciation. 2013 June 21‐25; Chicago (IL). American Diabetes Assosciation, 2013. [52‐LB]
Charbonnel 2005 {published data only}
-
- Charbonnel B, Schernthaner G, Brunetti P, Matthews DR, Urquhart R, Tan MH, et al. Long‐term efficacy and tolerability of add‐on pioglitazone therapy to failing monotherapy compared with addition of gliclazide or metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2005;48(6):1093‐104. [DOI: 10.1007/s00125-005-1751-1] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Matthews DR, Charbonnel BH, Hanefeld M, Brunetti P, Schernthaner G. Long‐term therapy with addition of pioglitazone to metformin compared with the addition of gliclazide to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, comparative study. Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews 2005;21(2):167‐74. [DOI: 10.1002/dmrr.478] - DOI - PubMed
Dei Cas 2017 {published data only}
-
- Dei Cas A, Spigoni V, Cito M, Aldigeri R, Ridolfi V, Marchesi E, et al. Vildagliptin, but not glibenclamide, increases circulating endothelial progenitor cell number: a 12‐month randomized controlled trial in patients with type 2 diabetes. Cardiovascular Diabetology 2017;16(1):27. [DOI: 10.1186/s12933-017-0503-0] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- NCT01822548. Effect of vildagliptin vs. glibenclamide on circulating endothelial progenitor cell number type 2 diabetes. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01822548 (accessed 26 June 2017).
Del Prato 2014 {published data only}
-
- Prato S, Camisasca R, Wilson C, Fleck P. Durability of the efficacy and safety of alogliptin compared with glipizide in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a 2‐year study. Diabetes Obesity Metabolism 2014;16(12):1239‐46. [DOI: ] - PubMed
-
- Prato S, Fleck P, Wilson C, Chaudhari P. Comparison of alogliptin and glipizide for composite endpoint of glycated haemoglobin reduction, no hypoglycaemia and no weight gain in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2016;18(6):623‐7. [DOI: ] - PubMed
-
- NCT00856284. Efficacy and safety of alogliptin plus metformin compared to glipizide plus metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (ENDURE). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00856284 (accessed 12 December 2016).
Del Prato 2015 {published data only}
-
- Abad Paniagua EJ, Casado Escribano P, Fernández Rodriguez JM, Morales Escobar FJ, Betegón Nicolás L, Sánchez‐Covisa J, et al. Cost‐effectiveness analysis of dapagliflozin compared to DPP4 inhibitors and other oral antidiabetic drugs in the treatment of type‐2 diabetes mellitus in Spain. Atencion Primaria 2015;47(8):505‐13. [DOI: 10.1016/j.aprim.2014.11.002] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Prato S, Nauck M, Durán‐Garcia S, Maffei L, Rohwedder K, Theuerkauf A, et al. Long‐term glycaemic response and tolerability of dapagliflozin versus a sulphonylurea as add‐on therapy to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: 4‐year data. Diabetes Obesity Metabolism 2015;17(6):581‐90. - PubMed
-
- Fenici P, Sternhufvud C, Cain V, Mukherjee J, Rohwedder K. Dapagliflozin added to metformin is effective in achieving combined improvements in HbA1c and weight without hypoglycaemia over 4 years. Diabetologia 2015;58:S355.
-
- Forst T, Rohwedder K, Sugg J, Johnsson E. Dapagliflozin decreases post‐prandial glucose without an increase in C‐peptide or insulin. Diabetes 2015;64:A324.
Derosa 2005 {published data only}
-
- Derosa G, Cicero AF, Gaddi AV, Ciccarelli L, Piccinni MN, Salvadeo S, et al. Long‐term effects of glimepiride or rosiglitazone in combination with metformin on blood pressure control in type 2 diabetic patients affected by the metabolic syndrome: a 12‐month, double‐blind, randomized clinical trial. Clinical Therapeutics 2005;27(9):1383‐91. - PubMed
-
- Derosa G, Gaddi A, Ciccarelli L, Fogari E, Ghelfi M, Ferrari I, et al. Long‐term effect of glimepiride and rosiglitazone on non‐conventional cardiovascular risk factors in metformin‐treated patients affected by metabolic syndrome: a randomized, double‐blind clinical trial. Journal of International Medical Research 2005;33(3):284‐94. - PubMed
-
- Derosa G, Gaddi AV, Piccinni MN, Ciccarelli L, Salvadeo S, Peros E, et al. Antithrombotic effects of rosiglitazone‐metformin versus glimepiride‐metformin combination therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome. Pharmacotherapy 2005;25(5):637‐45. - PubMed
-
- Derosa G, Gaddi AV, Piccinni MN, Salvadeo S, Ciccarelli L, Fogari E, et al. Differential effect of glimepiride and rosiglitazone on metabolic control of type 2 diabetic patients treated with metformin: a randomized, double‐blind, clinical trial. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2006;8(2):197‐205. - PubMed
Derosa 2009a {published data only}
-
- Derosa G, Maffioli P, Salvadeo SA, Ferrari I, Gravina A, Mereu R, et al. Direct comparison among oral hypoglycemic agents and their association with insulin resistance evaluated by euglycemic hyperinsulinemic clamp: the 60's study. Metabolism 2009;58(8):1059‐66. - PubMed
Derosa 2009b {published data only}
-
- Derosa G, D'Angelo A, Fogari E, Salvadeo S, Gravina A, Ferrari I, et al. Effects of nateglinide and glibenclamide on prothrombotic factors in naive type 2 diabetic patients treated with metformin: a 1‐year, double‐blind, randomized clinical trial. Internal Medicine (Tokyo, Japan) 2007;46(22):1837‐46. - PubMed
-
- Derosa G, D'Angelo A, Fogari E, Salvadeo S, Gravina A, Ferrari I, et al. Nateglinide and glibenclamide metabolic effects in naive type 2 diabetic patients treated with metformin. Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics 2009;34(1):13‐23. - PubMed
Derosa 2010 {published data only}
-
- Derosa G, Maffioli P, Salvadeo SA, Ferrari I, Ragonesi PD, Querci F, et al. Exenatide versus glibenclamide in patients with diabetes. Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics 2010;12(3):233‐40. - PubMed
Derosa 2011a {published data only}
-
- Derosa G, Putignano P, Bossi AC, Bonaventura A, Querci F, Franzetti IG, et al. Exenatide or glimepiride added to metformin on metabolic control and on insulin resistance in type 2 diabetic patients. European Journal of Pharmacology 2011;666(1‐3):251‐6. - PubMed
Derosa 2011b {published data only}
-
- Derosa G, Cicero AF, Fogari E, D'Angelo A, Bianchi L, Maffioli P. Pioglitazone compared to glibenclamide on lipid profile and inflammation markers in type 2 diabetic patients during an oral fat load. Hormone and Metabolic Research 2011;43(7):505‐12. - PubMed
Filozof 2010 {published data only}
-
- Filozof C, Gautier JF. A comparison of efficacy and safety of vildagliptin and gliclazide in combination with metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin alone: a 52‐week, randomized study. Diabetic Medicine 2010;27(3):318‐26. - PubMed
Gallwitz 2012a {published data only}
-
- Gallwitz B, Guzman J, Dotta F, Guerci B, Simó R, Basson BR, et al. Exenatide twice daily versus glimepiride for prevention of glycaemic deterioration in patients with type 2 diabetes with metformin failure (EUREXA): an open‐label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2012;379(9833):2270‐8. - PubMed
-
- Kazda C, Gallwitz B, Simó R, Guzmán JR, Kraus P, Nicolay C, et al. The European exenatide study of long‐term exenatide vs glimepiride for type 2 diabetes: rationale and patient characteristics. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2009;11(12):1131‐7. - PubMed
-
- NCT00359762. Exenatide versus glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00359762 (accessed 6 July 2017).
-
- Schernthaner G, Rosas‐Guzman J, Dotta F, Guerci B, Simo R, Festa A, et al. Treatment escalation options for patients with type 2 diabetes after failure of exenatide twice daily or glimepiride added to metformin: results from the prospective European Exenatide (EUREXA) study. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2015;17(7):689‐98. - PubMed
Gallwitz 2012b {published data only}
-
- Gallwitz B, Rosenstock J, Emser A, Eynatten M, Woerle HJ. Linagliptin is more effective than glimepiride at achieving a composite outcome of target HbA(1)c. International Journal of Clinical Practice 2013;67(4):317‐21. - PubMed
-
- Gallwitz B, Rosenstock J, Patel S, Eynatten M, Hehnke U, Mehlburger L, et al. Regardless of the degree of glycaemic control, linagliptin has lower hypoglycaemia risk than all doses of glimepiride, at all time points, over the course of a 2‐year trial. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2015;17(3):276‐84. - PubMed
-
- Gallwitz B, Rosenstock J, Rauch T, Bhattacharya S, Patel S, Eynatten M, et al. 2‐year efficacy and safety of linagliptin compared with glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin: a randomised, double‐blind, non‐inferiority trial. Lancet 2012;380(9840):475‐83. - PubMed
-
- Johansen OE, Boehm BO, Grill V, Torjesen PA, Bhattacharya S, Patel S, et al. C‐peptide levels in latent autoimmune diabetes in adults treated with linagliptin versus glimepiride: exploratory results from a 2‐year double‐blind, randomized, controlled study. Diabetes Care 2014;37(1):e11‐2. - PubMed
Gerich 2005 {published data only}
-
- CDJN608A US07. Multicenter, randomized, double‐blind, active controlled trial to compare the efficacy and safety of 104 weeks of nateglinide plus metformin vs glyburide plus metformin in drug naive subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus who have inadequate control with diet and exercise. www.novctrd.com/ctrdWebApp/clinicaltrialrepository/displayFile.do?trialR... (accessed 16 March 2017).
-
- Gerich J, Raskin P, Jean‐Louis L, Purkayastha D, Baron MA. PRESERVE‐beta: two‐year efficacy and safety of initial combination therapy with nateglinide or glyburide plus metformin. Diabetes Care 2005;28(9):2093‐9. - PubMed
-
- Schwarz SL, Gerich JE, Marcellari A, Jean‐Louis L, Purkayastha D, Baron MA. Nateglinide, alone or in combination with metformin, is effective and well tolerated in treatment‐naive elderly patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2008;10(8):652‐60. - PubMed
Göke 2013 {published data only}
-
- Cook W, Minervini G, Bryzinski B, Hirshberg B. Saxagliptin efficacy and safety in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus stratified by cardiovascular disease history and cardiovascular risk factors: analysis of 3 clinical trials. Postgraduate Medicine 2014;126(6):19‐32. - PubMed
-
- Goke B, Gallwitz B, Eriksson J, Hellqvist A, Gause‐Nilsson I. Saxagliptin is non‐inferior to glipizide in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled on metformin alone: a 52‐week randomised controlled trial. International Journal of Clinical Practice 2010;64(12):1619‐31. - PubMed
-
- Granstrom O, Bergenheim K, McEwan P, Sennfalt K, Henriksson M. Cost‐effectiveness of saxagliptin (Onglyza) in type 2 diabetes in Sweden. Primary Care Diabetes 2012;6(2):127‐36. - PubMed
-
- Göke B, Gallwitz B, Eriksson J G, Hellqvist Å, Gause‐Nilsson I. Saxagliptin vs glipizide as add‐on therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled on metformin alone: long‐term (52‐week) extension of a 52‐week randomised controlled trial. International Journal of Clinical Practice 2013;67(4):307‐16. - PubMed
-
- Mintz ML, Minervini G. Saxagliptin versus glipizide as add‐on therapy to metformin: assessment of hypoglycemia. Current Medical Research & Opinion 2014;30(5):761‐70. - PubMed
Hamann 2008 {published data only}
-
- GSK Study ID AVM100264. AVANDAMET versus metformin and sulphonylurea in people with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes. gsk‐studyregister.com/study/7254 (accessed 12 July 2017).
-
- Hamann A, Garcia‐Puig J, Paul G, Donaldson J, Stewart M. Comparison of fixed‐dose rosiglitazone/metformin combination therapy with sulphonylurea plus metformin in overweight Individuals with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin alone. Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes 2008;116(1):6‐13. - PubMed
-
- NCT00359112. AVANDAMET versus metformin and sulphonylurea in people with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT00359112 (accessed 12 July 2017).
Handelsman 2017 {published data only}
-
- Handelsman Y, Lauring B, Gantz I, Iredale C, O'Neill EA, Wei Z, et al. A randomized, double‐blind, non‐inferiority trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of omarigliptin, a once‐weekly DPP‐4 inhibitor, or glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin monotherapy. Current Medical Research and Opinion 2017;33(10):1861‐8. - PubMed
-
- MK‐3102‐016. Clinical study report P016. A study of the safety and efficacy of omarigliptin (MK‐3102) compared with glimepiride in participants with type 2 diabetes mellitus with inadequate glycemic control on metformin (MK‐3102‐016). merck.com/clinical‐trials/study.html?id=3102‐016&tab=access (accessed 6 March 2018).
-
- NCT01682759. A study of the safety and efficacy of omarigliptin (MK‐3102) compared with glimepiride in participants with type 2 diabetes mellitus with inadequate glycemic control on metformin (MK‐3102‐016). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT01682759 (accessed 6 March 2018).
Hollander 2017 {published data only}
-
- Hollander P, Liu J, Hill J, Johnson J, Jiang Z, Golm G, et al. Safety and efficacy of ertugliflozin compared to glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin: the VERTIS SU trial. Diabetologia 2017;60:S19‐S20.
-
- NCT01999218. Ertugliflozin vs. glimepiride in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) participants on metformin (MK‐8835‐002). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01999218 (accessed 1 March 2018).
Home 2009 {published data only}
-
- GSK Study ID BRL‐049653/231. BRL‐049653/231‐RECORD: rosiglitazone evaluated for cardiac outcomes and regulation of glycaemia in diabetes. gsk‐studyregister.com/study/7631 (accessed 1 April 2017).
-
- Home PD, Kahn SE, Jones NP, Noronha D, Beck‐Nielsen H, Viberti G. Experience of malignancies with oral glucose‐lowering drugs in the randomised controlled ADOPT (A Diabetes Outcome Progression Trial) and RECORD (Rosiglitazone Evaluated for Cardiovascular Outcomes and Regulation of Glycaemia in Diabetes) clinical trials. Diabetologia 2010;53(9):1838‐45. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Home PD, Pocock SJ, Beck‐Nielsen H, Curtis PS, Gomis R, Hanefeld M, et al. Rosiglitazone evaluated for cardiovascular outcomes in oral agent combination therapy for type 2 diabetes (RECORD): a multicentre, randomised, open‐label trial. Lancet 2009;373(9681):2125‐35. - PubMed
-
- Home PD, Pocock SJ, Beck‐Nielsen H, Gomis R, Hanefeld M, Dargie H, et al. Rosiglitazone evaluated for cardiac outcomes and regulation of glycaemia in diabetes (RECORD): study design and protocol. Diabetologia 2005;48(9):1726‐35. - PubMed
Leiter 2015 {published data only}
-
- Blonde L, Stenlof K, Fung A, Xie J, Canovatchel W, Meininger G. Effects of canagliflozin on body weight and body composition in patients with type 2 diabetes over 104 weeks. Postgraduate Medicine 2016;128(4):371‐80. - PubMed
-
- Cefalu WT, Leiter LA, Yoon K‐H, Arias P, Niskanen L, Xie J, et al. Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin versus glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin (CANTATA‐SU): 52 week results from a randomised, double‐blind, phase 3 non‐inferiority trial. Lancet 2013;382(9896):941‐50. - PubMed
-
- Desai M, Merton K, Davies MJ, Vijapurkar U, Balis D. Canagliflozin provides greater improvement in risk factors of metabolic syndrome (MetS) versus glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes and MetS on background metformin. Diabetologia 2016;59:S340‐1.
Maffioli 2013 {published data only}
-
- Maffioli P, Fogari E, D’Angelo A, Perrone T, Derosa G. Ultrasonography modifications of visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue after pioglitazone or glibenclamide therapy combined with rosuvastatin in type 2 diabetic patients not well controlled by metformin. European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology 2013;25(9):1113‐22. - PubMed
Matthews 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ahren B, Mathieu C, Bader G, Schweizer A, Foley JE. Efficacy of vildagliptin versus sulfonylureas as add‐on therapy to metformin: comparison of results from randomised controlled and observational studies. Diabetologia 2014;57(7):1304‐7. - PubMed
-
- Bader G, Geransar P, Schweizer A. Vildagliptin more effectively achieves a composite endpoint of HbA1c < 7 % without hypoglycaemia and weight gain compared with glimepiride after 2 years of treatment. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice 2013;100(3):e78‐81. - PubMed
-
- EudraCT 2004‐004559‐21. A multicenter, randomized, double‐blind, active controlled study to compare the long‐term effect (up to 5 years) of treatment with LAF237 50 mg bid to glimepiride up to 6 mg daily as add‐on therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin monotherapy. www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr‐search/trial/2004‐004559‐21/IT (accessed 11 March 2017).
Nauck 2013 {published data only}
-
- Blonde L, Russell‐Jones D. The safety and efficacy of liraglutide with or without oral antidiabetic drug therapy in type 2 diabetes: an overview of the LEAD 1‐5 studies. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2009;11 Suppl 3:26‐34. - PubMed
-
- Bode BW, Brett J, Falahati A, Pratley RE. Comparison of the efficacy and tolerability profile of liraglutide, a once‐daily human GLP‐1 analog, in patients with type 2 diabetes ≥65 and <65 years of age: a pooled analysis from phase III studies. American Journal of Geriatric Pharmacotherapy 2011;9(6):423‐33. - PubMed
-
- Buse JB, Garber A, Rosenstock J, Schmidt WE, Brett JH, Videbaek N, et al. Liraglutide treatment is associated with a low frequency and magnitude of antibody formation with no apparent impact on glycemic response or increased frequency of adverse events: results from the Liraglutide Effect and Action in Diabetes (LEAD) trials. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2011;96(6):1695‐702. - PubMed
-
- Fonseca VA, Devries JH, Henry RR, Donsmark M, Thomsen HF, Plutzky J. Reductions in systolic blood pressure with liraglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes: insights from a patient‐level pooled analysis of six randomized clinical trials. Journal of Diabetes and its Complications 2014;28(3):399‐405. - PMC - PubMed
NCT00367055 {published data only}
-
- GSK Study ID 101765. Rosiglitazone‐metformin combination versus metformin‐sulfonylurea combination on beta‐cell function in type 2 diabetes. gsk‐studyregister.com/study/2645 (accessed 28 June 2017).
-
- NCT00367055. Rosiglitazone‐metformin combination versus metformin‐sulfonylurea combination on beta‐cell function in type 2 diabetes. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT00367055 (accessed 28 June 2017).
Petrica 2009 {published data only}
-
- Petrica L, Petrica M, Vlad A, Jianu CD, Gluhovschi G, Ianculescu C, et al. Nephro‐ and neuroprotective effects of rosiglitazone versus glimepiride in normoalbuminuric patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial. Wiener Klinische Wochenschrift 2009;121(23‐24):765‐75. - PubMed
Petrica 2011 {published data only}
-
- Petrica L, Vlad A, Petrica M, Jianu CD, Gluhovschi G, Gadalean F, et al. Pioglitazone delays proximal tubule dysfunction and improves cerebral vessel endothelial dysfunction in normoalbuminuric people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice 2011;94(1):22‐32. - PubMed
Ridderstråle 2014 {published data only}
-
- Brice R, Spencer W, Asaro‐Harris A, Zeller C, Hach T, Salsali A, et al. Analysis of empagliflozin vs glimepiride by Quality and Outcomes Framework targets: post hoc analysis of a head‐to‐head study. Diabetic Medicine 2015;32:95‐6.
-
- Khunti K, Bingham‐Gardiner P, Hassan SW, Zeller C, Naderali E, Salsali A, et al. Efficacy and safety of empagliflozin compared with glimepiride in South Asian patients with type 2 diabetes in a head‐to‐head study. Diabetic Medicine 2015;32:96.
-
- Kohler S, Kaspers S, Salsali A, Zeller C, Woerle HJ. Effect of empagliflozin (EMPA) on bone fractures in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2DM). Diabetologia 2016;59:S26.
-
- NCT01167881. Efficacy and safety of empagliflozin (BI 10773) with metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01167881 (accessed 18 July 2017).
Ristic 2007 {published data only}
-
- CDJN608A2308. A multicenter, double‐blind, randomized, parallel‐group study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of nateglinide and gliclazide in combination with metformin, in type 2 diabetes patients inadequately controlled on maximally tolerated doses of metformin alone. www.novctrd.com/CtrdWeb/displaypdf.nov?trialresultid=1852 (accessed 17 July 2017).
-
- CDJN608A2308. Six month extension to a multicenter, double‐blind, randomized, parallel‐group study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of nateglinide and gliclazide in combination with metformin, in type 2 diabetes patients inadequately controlled on maximally tolerated doses of metformin alone. www.novctrd.com/CtrdWeb/displaypdf.nov?trialresultid=1850 (accessed 17 July 2017).
-
- Ristic S, Collober‐Maugeais C, Cressier F, Tang P, Pecher E. Nateglinide or gliclazide in combination with metformin for treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled on maximum doses of metformin alone: 1‐year trial results. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2007;9(4):506‐11. - PubMed
Schernthaner 2015 {published data only}
-
- NCT01006603. Saxagliptin compared to glimepiride in elderly type 2 diabetes patients, with inadequate glycemic control on metformin (GENERATION). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01006603 (accessed 2 August 2017).
-
- Perl S, Cook W, Wei C, Ohman P, Hirshberg B. Effects of glimepiride versus saxagliptin on beta‐cell function and hypoglycemia: a post hoc analysis in older patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin. Clinical Therapeutics 2016;38(12):2578‐88. - PubMed
-
- Perl S, Cook W, Wei C, Ohman P, Hirshberg B. Low beta‐cell function at baseline is associated with higher rates of hypoglycemia in response to treatment with glimepiride in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin. Diabetes 2015;64:A319.
-
- Schernthaner G, Durán‐Garcia S, Hanefeld M, Langslet G, Niskanen L, Östgren CJ, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of saxagliptin compared with glimepiride in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, controlled study (GENERATION). Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2015;17(7):630‐8. - PubMed
Seck 2010 {published data only}
-
- Krobot KJ, Ferrante SA, Davies MJ, Seck T, Meininger GE, Williams‐Herman D, et al. Lower risk of hypoglycemia with sitagliptin compared to glipizide when either is added to metformin therapy: a pre‐specified analysis adjusting for the most recently measured HbA(1c) value. Current Medical Research and Opinion 2012;28(8):1281‐7. - PubMed
-
- NCT00094770. An investigational drug study in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (0431‐024). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT00094770 (accessed 14 July 2017).
-
- Nauck MA, Meininger G, Sheng D, Terranella L, Stein PP. Efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitor, sitagliptin, compared with the sulfonylurea, glipizide, in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin alone: a randomized, double‐blind, non‐inferiority trial. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2007;9(2):194‐205. - PubMed
-
- Seck T, Nauck M, Sheng D, Sunga S, Davies MJ, Stein PP, et al. Safety and efficacy of treatment with sitagliptin or glipizide in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin: a 2‐year study. International Journal of Clinical Practice 2010;64(5):562‐76. - PubMed
Vaccaro 2017 {published data only}
-
- Chilelli. Long‐term effect of pioglitazone vs glimepiride on lipoprotein oxidation in patients with type 2 diabetes: a prospective randomized study. Manuscript draft (accessed 19 March 2018). - PubMed
-
- NCT00700856. Thiazolidinediones or sulphonylureas and cardiovascular accidents intervention trial (TOSCA IT). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00700856 (accessed 9 October 2017).
-
- Vaccaro O, Masulli M, Bonora E, Prato S, Giorda CB, Maggioni AP, et al. Addition of either pioglitazone or a sulfonylurea in type 2 diabetic patients inadequately controlled with metformin alone: impact on cardiovascular events. A randomized controlled trial. Nutrition, Metabolism, and Cardiovascular Diseases 2012;22(11):997‐1006. - PubMed
-
- Vaccaro O, Masulli M, Nicolucci A, Bonora E, Prato S, Maggioni AP, et al. Effects on the incidence of cardiovascular events of the addition of pioglitazone versus sulfonylureas in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin (TOSCA.IT): a randomised, multicentre trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinology 2017;5(11):887‐97. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
ACCORD 2007 {published data only}
-
- Buse JB, Bigger JT, Byington RP, Cooper LS, Cushman WC, Friedewald WT, et al. Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes (ACCORD) trial: design and methods. American Journal of Cardiology 2007;99(12a):21i‐33i. - PubMed
-
- NCT00000620. Action to control cardiovascular risk in diabetes (ACCORD). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00000620 (accessed 3 March 2018).
Alsharidah 2018 {published data only}
Araki 2015 {published data only}
-
- Araki E, Tanizawa Y, Tanaka Y, Taniguchi A, Koiwai K, Kim G, et al. Long‐term treatment with empagliflozin as add‐on to oral antidiabetes therapy in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2015;17(7):665‐74. - PubMed
-
- NCT01368081. Empagliflozin (BI 10773) comprehensive add‐on study in Japanese subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01368081 (accessed 3 March 2018).
Bermudez‐Pirela 2007 {published data only}
-
- Bermudez‐Pirela VJ, Cano C, Medina MT, Souki A, Lemus MA, Leal EM, et al. Metformin plus low‐dose glimeperide significantly improves Homeostasis Model Assessment for insulin resistance (HOMA(IR)) and beta‐cell function (HOMA(beta‐cell)) without hyperinsulinemia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. American Journal of Therapeutics 2007;14(2):194‐202. - PubMed
Berndt‐Zipfel 2013 {published data only}
-
- Berndt‐Zipfel C, Michelson G, Dworak M, Mitry M, Loffler A, Pfutzner A, et al. Vildagliptin in addition to metformin improves retinal blood flow and erythrocyte deformability in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus ‐ results from an exploratory study. Cardiovascular Diabetology 2013;12:59. - PMC - PubMed
-
- NCT01565096. Effect of adding vildagliptin on beta cell function and cardiovascular risk markers in patients with moderate metabolic control during metformin monotherapy. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01565096 (accessed 3 March 2018).
Bode 2013 {published data only}
-
- Bode B, Stenlof K, Sullivan D, Fung A, Usiskin K. Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin treatment in older subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized trial. Hospital Practice (1995) 2013;41(2):72‐84. - PubMed
-
- NCT01106651. A safety and efficacy study of canagliflozin in older patients (55 to 80 years of age) with type 2 diabetes mellitus. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01106651 (accessed 3 March 2018).
Bruce 2006 {published data only}
-
- Bruce S, Park JS, Fiedorek FT, Howlett HC. Beta‐cell response to metformin‐glibenclamide combination tablets (Glucovance) in patients with type 2 diabetes. International Journal of Clinical Practice 2006;60(7):783‐90. - PubMed
-
- NCT00035568. A research study to assess the mechanism by which glucovance, metformin, and glyburide work to control glucose levels In patients with type 2 diabetes. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00035568 (accessed 3 March 2018).
Charbonnel 2006 {published data only}
-
- Charbonnel B, Karasik A, Liu J, Wu M, Meininger G. Efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitor sitagliptin added to ongoing metformin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin alone. Diabetes Care 2006;29(12):2638‐43. - PubMed
-
- NCT00086515. Metformin add‐on study in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (0431‐020)(COMPLETED). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00086515 (accessed 3 March 2018).
Cryer 2005 {published data only}
-
- Cryer DR, Nicholas SP, Henry DH, Mills DJ, Stadel BV. Comparative outcomes study of metformin intervention versus conventional approach the COSMIC Approach Study. Diabetes Care 2005;28(3):539‐43. - PubMed
CTRI/2013/02/003417 {published data only}
-
- CTRI/2013/02/003417. Restudy of the PURSE HIS Population for the prevalence of risk factors causing blood vessel damage to heart muscle, brain tissue or peripheral tissue and to give advice on diet, exercise and if necessary small dose of drug to prevent conversion of pre‐diabetes to diabetes. www.ctri.nic.in/Clinicaltrials/pdf_generate.php?trialid=6005&EncHid=... (accessed 9 March 2018).
Derosa 2015 {published data only}
-
- Derosa G, D'Angelo A, Maffioli P. Sitagliptin in type 2 diabetes mellitus: efficacy after five years of therapy. Pharmacological Research 2015;100:127‐34. - PubMed
EUCTR2004‐002549‐11‐FI {published data only}
-
- Eudract: 2004‐002549‐11. An open, multi‐centre and long‐term extension study to evaluate the safety and tolerability of oral tesaglitazar therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes ‐ GALLEX 1. www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr‐search/search?query=eudract_number:200... (accessed 3 March 2018).
EUCTR2006‐001240‐30‐BE {published data only}
-
- Eudract: 2006‐001240‐30. Long term double blind comparison of gliclazide MR (30 to 120 mg daily per os) and rosiglitazone (4 to 8 mg daily per os) given in combination with metformin in type 2 diabetic patients. A 2‐year international, multicentre, randomised, double‐blind, parallel‐group study followed by a 2‐year double blind extension ‐ ENDORSE. www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr‐search/search?query=eudract_number:200... (accessed 3 March 2018).
EUCTR2009‐014727‐23‐IT {published data only}
-
- Eudract: 2009‐014727‐23. Multi‐center, randomized, open‐label, two‐parallel arm, intervention trial comparing DPP‐IV inhibitor vildagliptin with glibenclamide (glyburide) in achieving and maintaining good blood glucose control in type 2 diabetic patients in treatment failure with metformin alone ‐ Long‐term clinical effectiveness of DPP‐IV inhibitors. www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr‐search/search?query=eudract_number:200... (accessed 3 March 2018).
EUCTR2009‐017524‐36‐HU {published data only}
-
- Eudract: 2009‐017524‐36. A phase III, multicenter, double‐blind, active‐controlled, 52‐week extension study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of dutogliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus receiving background treatment with glimepiride alone or in combination with metformin or with pioglitazone alone. www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr‐search/search?query=eudract_number:200... (accessed 3 March 2018).
Gregorio 1989 {published data only}
-
- Gregorio F, Ambrosi F, Angelici F, Cristallini S, Dini FL, Vespasiani G, et al. Body mass index, blood lactate and therapeutic effectiveness of metformin in type II diabetes mellitus. Medicina (Florence, Italy) 1989;9(2):200‐4. - PubMed
Haering 2015 {published data only}
-
- Haering HU, Merker L, Christiansen AV, Roux F, Salsali A, Kim G, et al. Empagliflozin as add‐on to metformin plus sulphonylurea in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice 2015;110(1):82‐90. - PubMed
-
- NCT01289990. Safety and efficacy of empagliflozin (BI 10773) and sitagliptin versus placebo over 76 weeks in patients with type 2 diabetes. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01289990 (accessed 3 March 2018).
-
- Roden M, Merker L, Christiansen AV, Roux F, Salsali A, Kim G, et al. Safety, tolerability and effects on cardiometabolic risk factors of empagliflozin monotherapy in drug‐naive patients with type 2 diabetes: a double‐blind extension of a phase III randomized controlled trial. Cardiovascular Diabetology 2015;14:154. - PMC - PubMed
Hassanein 2014 {published data only}
-
- Hassanein M, Abdallah K, Schweizer A. A double‐blind, randomized trial, including frequent patient‐physician contacts and Ramadan‐focused advice, assessing vildagliptin and gliclazide in patients with type 2 diabetes fasting during Ramadan: the STEADFAST study. Vascular Health and Risk Management 2014;10:319‐26. - PMC - PubMed
Heller 2018 {published data only}
-
- Heller SR, Pratley RE, Sinclair A, Festa A, Kiljanski J, Brusko CS, et al. Glycaemic outcomes of an individualized treatment approach for older vulnerable patients: a randomized, controlled study in type 2 diabetes mellitus (IMPERIUM). Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2018;20(1):148‐56. - PMC - PubMed
-
- NCT02072096. A comparison of two treatment strategies in older participants with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) (IMPERIUM). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02072096 (accessed 3 March 2018).
Hermann 2001 {published data only}
-
- Hermann LS, Kalen J, Katzman P, Lager I, Nilsson A, Norrhamn O, et al. Long‐term glycaemic improvement after addition of metformin to insulin in insulin‐treated obese type 2 diabetes patients. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2001;3(6):428‐34. - PubMed
Inagaki 2013 {published data only}
-
- Inagaki N, Watada H, Murai M, Kagimura T, Gong Y, Patel S, et al. Linagliptin provides effective, well‐tolerated add‐on therapy to pre‐existing oral antidiabetic therapy over 1 year in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2013;15(9):833‐43. - PubMed
-
- NCT01204294. Comprehensive add on study in Japan. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01204294 (accessed 3 March 2018).
Iqbal 2014 {published data only}
ISRCTN19750520 {published data only}
-
- ISRCTN19750520. Reduced urine albumin excretion in community based collaborative care in elderly Chinese with type 2 diabetes. www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN19750520 (accessed 9 March 2018).
ISRCTN41840459 {published data only}
-
- ISRCTN41840459. A study to assess the release profiles from fixed combination tablets (gliclazide MR/metformin). www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN41840459 (accessed 3 March 2018).
Jackson 1987 {published data only}
-
- Jackson RA, Hawa MI, Jaspan JB, Sim BM, Disilvio L, Featherbe D, et al. Mechanism of metformin action in non‐insulin‐dependent diabetes. Diabetes 1987;36(5):632‐40. - PubMed
Javaid 2007 {published data only}
-
- Javaid A, Hasan R, Zaib A, Mansoor S. A comparative study of the effects of hypoglycemic agents on serum electrolytes in the diabetic patients. Pakistan Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2007;20(1):67‐71. - PubMed
Johansen 2007 {published data only}
-
- Johansen OE, Gullestad L, Blaasaas KG, Orvik E, Birkeland KI. Effects of structured hospital‐based care compared with standard care for type 2 diabetes‐The Asker and Baerum Cardiovascular Diabetes Study, a randomized trial. Diabetic Medicine 2007;24(9):1019‐27. - PubMed
-
- NCT00133718. A 2 year trial of patients with type 2 diabetes focusing on cardiovascular diagnostics and metabolic control. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00133718?term=NCT00133718&rank=1 (accessed 3 March 2018).
JPRN‐UMIN000005327 {published data only}
-
- JPRN‐UMIN000005327. Comparisons of oral agents to standardize treatment for diabetes in Japan. upload.umin.ac.jp/cgi‐open‐bin/ctr_e/ctr_view.cgi?recptno=R000006064 (accessed 3 March 2018).
Kala 2017 {published data only}
-
- Kala 2017. A comparative study of efficacy and safety among metformin with sitagliptin, metformin with voglibose, and metformin with glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research 2017;Vol 10(Issue 12):313‐16.
Malha 2014 {published data only}
Marre 2002 {published data only}
-
- Marre M, Howlett H, Lehert P, Allavoine T. Improved glycaemic control with metformin‐glibenclamide combined tablet therapy (Glucovance) in type 2 diabetic patients inadequately controlled on metformin. Diabetic Medicine 2002;19(8):673‐80. - PubMed
Meneghini 2010 {published data only}
-
- Meneghini LF, Traylor L, Schwartz SL. Improved glycemic control with insulin glargine versus pioglitazone as add‐on therapy to sulfonylurea or metformin in patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocrine Practice 2010;16(4):588‐99. - PubMed
Moon 2014 {published data only}
-
- Moon JS, Ha KS, Yoon JS, Lee HW, Lee HC, Won KC. The effect of glargine versus glimepiride on pancreatic beta‐cell function in patients with type 2 diabetes uncontrolled on metformin monotherapy: open‐label, randomized, controlled study. Acta Diabetologica 2014;51(2):277‐85. - PubMed
-
- NCT00562172. Insulin glargine (lantus) vs sulfonylurea (SU) for BETA cell function (BETA study). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00562172 (accessed 3 March 2018).
Morikawa 2011 {published data only}
-
- Morikawa A, Ishizeki K, Iwashima Y, Yokoyama H, Muto E, Oshima E, et al. Pioglitazone reduces urinary albumin excretion in renin‐angiotensin system inhibitor‐treated type 2 diabetic patients with hypertension and microalbuminuria: the APRIME study. Clinical and Experimental Nephrology 2011;15(6):848‐53. - PubMed
Nauck 2006 {published data only}
-
- NCT01511172. Effect of liraglutide as add‐on to metformin compared to either liraglutide or metformin alone, or to a combination of metformin and a SU (sulphonylurea) agent in subjects with type 2 diabetes. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01511172 (accessed 3 March 2018).
-
- Nauck MA, Hompesch M, Filipczak R, Le TD, Zdravkovic M, Gumprecht J. Five weeks of treatment with the GLP‐1 analogue liraglutide improves glycaemic control and lowers body weight in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes 2006;114(8):417‐23. - PubMed
NCT00269061 {published data only}
-
- NCT00269061. An exploratory MRI study in type 2 diabetic subjects: a randomized, double‐blinded, placebo‐controlled trial to evaluate the measurement of fluid volumes by MRI in the lower extremities of subjects receiving pioglitazone. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00269061 (accessed 3 March 2018).
NCT00449605 {published data only}
-
- NCT00449605. A glycemic control evaluation of glimepiride versus rimonabant on top of metformin in type 2 diabetes (ALLEGRO). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00449605?term=NCT00449605&rank=1 (accessed 3 March 2018).
NCT00518882 {published data only}
-
- NCT00518882. Effect of liraglutide or exenatide added to an ongoing treatment on blood glucose control in subjects with type 2 diabetes (LEAD‐6). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00518882 (accessed 9 March 2018).
NCT00543751 {published data only}
-
- NCT00543751. Placebo controlled metformin and sulfonylurea combination study in patients with type 2 diabetes (0767‐025). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00543751 (accessed 9 March 2018).
NCT00839527 {published data only}
-
- NCT00839527. A randomized, double‐blind, placebo and active‐controlled, parallel‐group, multicenter study to determine the efficacy and safety of albiglutide administered in combination with metformin and glimepiride compared with metformin plus glimepiride and placebo and with metformin plus glimepiride and pioglitazone in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00839527 (accessed 3 March 2018).
NCT00909597 {published data only}
-
- NCT00909597. A study of taspoglutide versus pioglitazone in patients with type 2 diabetes. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00909597 (accessed 3 March 2018).
NCT00947557 {published data only}
-
- NCT00947557. A phase III, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, multicenter study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of dutogliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus on background treatment with glimepiride with or without metformin. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00947557 (accessed 9 March 2018).
NCT01087567 {published data only}
-
- NCT01087567. INSPIRE diabetes study: basal bolus insulin as primary treatment of type 2 diabetes. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01087567 (accessed 9 March 2018).
NCT01106625 {published data only}
-
- NCT01106625. The CANTATA‐MSU Trial (canagliflozin treatment and trial analysis ‐ metformin and sulphonylurea). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01106625 (accessed 3 March 2018).
NCT01426737 {published data only}
-
- NCT01426737. The Swiss glucose variability study. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01426737 (accessed 26 June 2017).
NCT01455883 {published data only}
-
- NCT01455883. A study to evaluate ITCA 650 compared to glimepiride for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01455883 (accessed 3 March 2018).
NCT01481116 {published data only}
-
- NCT01481116. Efficacy and safety of TAK‐875 compared to glimepiride when used with metformin in participants with type 2 diabetes. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/results/NCT01481116 (accessed 26 June 2017).
NCT01593137 {published data only}
-
- NCT01593137. A long‐term, randomized, open‐labeled, parallel‐group trial to compare the effects of liraglutide and sulphonylurea (glimepiride) both in combination with metformin on clinical, endothelial and image markers of cardiovascular risk in patients with type 2 diabetes. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01593137 (accessed 3 March 2018).
NCT02244164 {published data only}
-
- NCT02244164. Pathophysiological study of the increase in pancreatic volume in type 2 diabetes treatments. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02244164 (accessed 3 March 2018).
NCT02462369 {published data only}
-
- NCT02462369. Saxagliptin's effects on microalbuminuria improvement in type 2 diabetic patients. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02462369 (accessed 28 February 2018).
NCT02587741 {published data only}
-
- NCT02587741. Comparison of diabetes retinopathy among type 2 diabetic patients treated with different regimens (CORRECT). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02587741 (accessed 3 March 2018).
NCT02616666 {published data only}
-
- NCT02616666. A pragmatic trial to evaluate the comparative effectiveness between dapagliflozin and standard of care in type 2 diabetes patients (DECIDE Study). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02616666 (accessed 9 March 2018).
NCT03060980 {published data only}
-
- NCT03060980. Comparison of efficacy, safety, and tolerability of ITCA 650 to empagliflozin and glimepiride as add‐on metformin. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03060980 (accessed 9 March 2018).
Onuchin 2010 {published data only}
-
- Onuchin SG, Elsukova OS, Solov'ev OV, Onuchina EL. Capabilities of hypoglycemic therapy in women with decompensated type 2 diabetes mellitus. Terapevticheskii Arkhiv 2010;82(8):34‐41. - PubMed
Rosenstock 2006 {published data only}
-
- Rosenstock J, Sugimoto D, Strange P, Stewart JA, Soltes‐Rak E, Dailey G. Triple therapy in type 2 diabetes: insulin glargine or rosiglitazone added to combination therapy of sulfonylurea plus metformin in insulin‐naive patients. Diabetes Care 2006;29(3):554‐9. - PubMed
Rosenstock 2018 {published data only}
-
- NCT02033889. A study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of ertugliflozin in participants with type 2 diabetes mellitus and inadequate glycemic control on metformin monotherapy (MK‐8835‐007). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02033889 (accessed 28 February 2018).
-
- Rosenstock J, Frias J, Pall D, Charbonnel B, Pascu R, Saur D, et al. Effect of ertugliflozin on glucose control, body weight, blood pressure and bone density in type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled on metformin monotherapy (VERTIS MET). Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2018;20(3):520‐9. - PubMed
Rubin 2008 {published data only}
-
- NCT00095030. Study comparing muraglitazar with glimepiride in type 2 diabetics who are not controlled with metformin alone. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00095030 (accessed 26 June 2017).
-
- Rubin CJ, Ledeine JM, Fiedorek FT. Improvement of glycaemic and lipid profiles with muraglitazar plus metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: an active‐control trial with glimepiride. Diabetes & Vascular Disease Research 2008;5(3):168‐76. - PubMed
Shankar 2017 {published data only}
-
- NCT01755156. A study to evaluate the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of the addition of omarigliptin (MK‐3102) to participants with type 2 diabetes mellitus who have inadequate glycemic control on metformin therapy (MK‐3102‐024). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01755156 (accessed 28 February 2018).
-
- Shankar RR, Inzucchi SE, Scarabello V, Gantz I, Kaufman KD, Lai E, et al. A randomized clinical trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of the once‐weekly dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitor omarigliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin monotherapy. Current Medical Research and Opinion 2017;33(10):1853‐60. - PubMed
Tolman 2009 {published data only}
-
- NCT00494312. Safety study of pioglitazone compared to glyburide on liver function. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00494312?term=NCT00494312&rank=1 (accessed 3 March 2018).
-
- Tolman KG, Freston JW, Kupfer S, Perez A. Liver safety in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with pioglitazone: results from a 3‐year, randomized, comparator‐controlled study in the US. Drug Safety 2009;32(9):787‐800. - PubMed
UKPDS 1998 {published data only}
-
- ISRCTN75451837. UK prospective diabetes study ‐ post study monitoring (PSM) and cohort follow‐up (CFU). www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN75451837 (accessed 9 March 2018).
-
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood‐glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet 1998;352(9131):837‐53. - PubMed
Weissman 2014 {published data only}
-
- Weissman PN, Carr MC, Ye J, Cirkel DT, Stewart M, Perry C, et al. HARMONY 4: randomised clinical trial comparing once‐weekly albiglutide and insulin glargine in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin with or without sulfonylurea. Diabetologia 2014;57(12):2475‐84. - PubMed
Yki‐Järvinen 1999 {published data only}
-
- Yki‐Järvinen H, Ryysy L, Nikkilä K, Tulokas T, Vanamo R, Heikkilä M. Comparison of bedtime insulin regimens in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. A randomized, controlled trial. Annals of Internal Medicine 1999;130(5):389‐96. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Müller‐Wieland 2018 {published data only}
-
- NCT02471404. Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin and dapagliflozin plus saxagliptin in combination with metformin in type 2 diabetes patients compared with sulphonylurea. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02471404 (accessed 28 February 2018).
NCT02564926 {published data only}
-
- NCT02564926. Foxiga Korea local phase 4 study (BEYOND). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02564926 (accessed 28 February 2018).
References to ongoing studies
EUCTR2011‐003335‐63‐IT {published data only}
-
- EUCTR2011‐003335‐63‐IT. Effects of liraglutide on ß‐cell function in type 2 diabetic patients with secondary failure to oral hypoglycemic agents. A randomized, controlled, parallel groups, open‐label, phase II study. apps.who.int/trialsearch/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=EUCTR2011‐003335‐63‐IT (accessed 28 February 2018).
EUCTR2012‐000152‐34‐IT {published data only}
-
- EUCTR2012‐000152‐34‐IT. Evaluation of the effect of treatment with DPP‐4 inhibitor on endothelial function versus sulphonylurea on markers of oxidative stress and inflammation and platelet function in patients with diabetes mellitus type 2 in primary failure with metformin and with HbA1c values below 8, 5%. apps.who.int/trialsearch/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=EUCTR2012‐000152‐34‐IT (accessed 28 February 2018).
JPRN‐UMIN000008815 {published data only}
-
- JPRN‐UMIN000008815. The effect of DPP‐4 inhibitor on pancreatic beta cell function and renal function in type 2 diabetic patients. upload.umin.ac.jp/cgi‐open‐bin/ctr_e/ctr_view.cgi?recptno=R000010271 (accessed 28 February 2018).
NCT01243424 {published data only}
-
- NCT01243424. CAROLINA: Cardiovascular outcome study of linagliptin versus glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01243424 (accessed 28 February 2018).
NCT01794143 {published data only}
-
- NCT01794143. A comparative effectiveness study of major glycemia‐lowering medications for treatment of type 2 diabetes (GRADE). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01794143 (accessed 28 February 2018).
NCT02142309 {published data only}
-
- NCT02142309. Glycemic durability after metformin failure (AMAZING). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02142309 (accessed 28 February 2018).
NCT02730377 {published data only}
-
- NCT02730377. Efficacy in controlling glycaemia with Victoza® (liraglutide) as add‐on to metformin vs. OAD's as add‐on to metformin after up to 104 weeks of treatment in subjects with type 2 diabetes (LIRA‐PRIME). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02730377 (accessed 28 February 2018).
NCT02769481 {published data only}
-
- NCT02769481. Safety and efficacy of bexagliflozin compared to glimepiride as add‐on therapy to metformin in type 2 diabetes subjects. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02769481 (accessed 28 February 2018).
NCT03332771 {published data only}
-
- NCT03332771. Efficacy and safety of sotagliflozin versus glimepiride and placebo in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus that are taking metformin monotherapy (SOTA‐GLIM). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03332771 (accessed 9 March 2018).
Additional references
ADA 2003
-
- Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Report of the expert committee on the diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2003;26(Suppl 1):S5‐20. - PubMed
ADA 2008
-
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes ‐ 2008. Diabetes Care 2008;31(Suppl 1):S12‐54. [PUBMED: 18165335] - PubMed
ADA 2016
-
- American Diabetes Association. 7. Approaches to glycemic treatment. Diabetes Care 2016;39(Suppl 1):S52‐9. [PUBMED: 26696682] - PubMed
ADA 2019
-
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes ‐ 2019. care.diabetesjournals.org/content/diacare/suppl/2018/12/17/42.Supplement... (accessed 16 February 2019).
ADOPT 2006
-
- Kahn SE, Haffner SM, Heise MA, Herman WH, Holman RR, Jones NP, et al. Glycemic durability of rosiglitazone, metformin, or glyburide monotherapy. New England Journal of Medicine 2006;355(23):2427‐43. [PUBMED: 17145742] - PubMed
Albarran 2013
-
- Albarran OG, Ampudia‐Blasco FJ. Dapagliflozin, the first SGLT‐2 inhibitor in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Medicina Clinica 2013;141 Suppl 2:36‐43. - PubMed
Almdal 2004
-
- Almdal T, Scharling H, Jensen JS, Vestergaard H. The independent effect of type 2 diabetes mellitus on ischemic heart disease, stroke, and death: a population‐based study of 13,000 men and women with 20 years of follow‐up. Archives of Internal Medicine 2004;164(13):1422‐6. [PUBMED: 15249351] - PubMed
Altman 2003
Alvares 2015
-
- Alvares J, Araujo VE, Izidoro JB, Diniz LM, Nascimento RC, Silva MR, et al. Efficacy and safety of antidiabetic drugs available on Brazilian public health system (Sus) ‐ regular insulin, NPH insulin, metformin, glibenclamide and gliclazide ‐ In treatment of type 2 diabetes (T2DM) ‐ systematic review and meta‐analysis. Value in Health 2015;18(7):A862.
Amate 2015
-
- Amate JM, Lopez‐Cuadrado T, Almendro N, Bouza C, Saz‐Parkinson Z, Rivas‐Ruiz R, et al. Effectiveness and safety of glimepiride and iDPP4, associated with metformin in second line pharmacotherapy of type 2 diabetes mellitus: systematic review and meta‐analysis. International Journal of Clinical Practice 2015;69(3):292‐304. - PMC - PubMed
Andersen 2016
Aylsworth 2014
-
- Aylsworth A, Dean Z, VanNorman C, Nkemdirim Okere A. Dapagliflozin for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Annals of Pharmacotherapy 2014;48(9):1202‐8. - PubMed
Bailey 1996
-
- Bailey CJ, Turner RC. Metformin. New England Journal of Medicine 1996;334(9):574‐9. [PUBMED: 8569826] - PubMed
Bell 2013
-
- Bell ML, McKenzie JE. Designing psycho‐oncology randomised trials and cluster randomised trials: variance components and intra‐cluster correlation of commonly used psychosocial measures. Psycho‐oncology 2013;22:1738‐47. - PubMed
Bellary 2011
-
- Bellary S. For type 2 diabetes poorly controlled by metformin monotherapy, the addition of any non‐insulin antidiabetic drug reduces HbA1c to a similar extent, but with differing effects on weight and hypoglycaemic risk. Evidence‐based Medicine 2011;16(2):39‐40. - PubMed
Belsey 2008
-
- Belsey J, Krishnarajah G. Glycaemic control and adverse events in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with metformin + sulphonylurea: a meta‐analysis. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2008;10 Suppl 1:1‐7. - PubMed
Boutron 2014
-
- Boutron I, Altman DG, Hopewell S, Vera‐Badillo F, Tannock I, Ravaud P. Impact of spin in the abstracts of articles reporting results of randomized controlled trials in the field of cancer: the SPIIN randomized controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2014;32:4120‐6. - PubMed
Buch 2011
-
- Buch MH, Aletaha D, Emery P, Smolen JS. Reporting of long‐term extension studies: lack of consistency calls for consensus. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2011;70(6):886‐90. - PubMed
Chan 2015
-
- Chan SP, Colagiuri S. Systematic review and meta‐analysis of the efficacy and hypoglycemic safety of gliclazide versus other insulinotropic agents. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice 2015;110(1):75‐81. - PubMed
CONSORT
-
- The CONSORT statement. www.consort‐statement.org (accessed 19 may 2016).
Corbett 2014
-
- Corbett MS, Higgins JP, Woolacott NF. Assessing baseline imbalance in randomised trials: implications for the Cochrane risk of bias tool. Research Synthesis Methods 2014;5:79‐85. - PubMed
Dai 2014
-
- Dai X, Wang H, Jing Z, Fu P. The effect of a dual combination of noninsulin antidiabetic drugs on lipids: a systematic review and network meta‐analysis. Current Medical Research and Opinion 2014;30(9):1777‐86. - PubMed
Deacon 2015
-
- Deacon CF, Lebovitz HE. A comparative review of DPP‐4 inhibitors and sulphonylureas. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2015;18(4):333‐47. [PUBMED: 26597596] - PubMed
Deeks 2003
-
- Deeks JJ, Dinnes J, D'Amico R, Sowden AJ, Sakarovitch C, Song F, et al. Evaluating non‐randomised intervention studies. Health Technology Assessment (Winchester, England) 2003;7(27):iii‐x, 1‐173. [PUBMED: 14499048] - PubMed
Deeks 2017
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JP, Altman DG (editors): on behalf of the Cochrane Statistical Methods Group. Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses. In: Higgins JPT, Churchill R, Chandler J, Cumpston MS (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 5.2.0 (updated June 2017), Cochrane, 2017. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
DeFronzo 1999
-
- DeFronzo RA. Pharmacologic therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Annals of Internal Medicine 1999;131(4):281‐303. [PUBMED: 10454950] - PubMed
Evans 2006
-
- Evans JM, Ogston SA, Emslie‐Smith A, Morris AD. Risk of mortality and adverse cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes: a comparison of patients treated with sulfonylureas and metformin. Diabetologia 2006;49(5):930‐6. [PUBMED: 16525843] - PubMed
Fleming 2015
Foroutan 2016
-
- Foroutan N, Muratov S, Levine M. Safety and efficacy of dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitors vs sulfonylurea in metformin‐based combination therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus: systematic review and meta‐analysis. Clinical and Investigative Medicine, Medecine Clinique et Experimentale 2016;39(2):E48‐62. - PubMed
Geng 2015
-
- Geng J, Yu H, Mao Y, Zhang P, Chen Y. Cost effectiveness of dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitors for type 2 diabetes. Pharmaco Economics 2015;33(6):581‐97. - PubMed
Goring 2014
-
- Goring S, Hawkins N, Wygant G, Roudaut M, Townsend R, Wood I, et al. Dapagliflozin compared with other oral anti‐diabetes treatments when added to metformin monotherapy: a systematic review and network meta‐analysis. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2014;16(5):433‐42. - PubMed
GRADEproGDT 2015 [Computer program]
-
- McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime). GRADEproGDT. Hamilton (ON): McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime), 2015 (accessed 28 February 2018).
Gu 2015
-
- Gu S, Deng J, Shi L, Mu Y, Dong H. Cost‐effectiveness of saxagliptin vs glimepiride as a second‐line therapy added to metformin in type 2 diabetes in China. Journal of Medical Economics 2015;18(10):808‐20. - PubMed
Gulliford 2004
-
- Gulliford M, Latinovic R. Mortality in type 2 diabetic subjects prescribed metformin and sulphonylurea drugs in combination: cohort study. Diabetes/metabolism Research and Reviews 2004;20(3):239‐45. [PUBMED: 15133756] - PubMed
Guthrie 2015
-
- Guthrie RM. Clinical use of dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 and sodium‐glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in combination therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Postgraduate Medicine 2015;127(5):463‐79. - PubMed
Harrower 2000
-
- Harrower AD. Comparative tolerability of sulphonylureas in diabetes mellitus. Drug Safety 2000;22(4):313‐20. [PUBMED: 10789825] - PubMed
Harrower 2000a
-
- Harrower A. Gliclazide modified release: from once‐daily administration to 24‐hour blood glucose control. Metabolism: Clinical and Experimental 2000;49(10 Suppl 2):7‐11. [PUBMED: 11078469] - PubMed
Hart 2012
Hemmingsen 2011
-
- Hemmingsen B, Lund SS, Gluud C, Vaag A, Almdal T, Hemmingsen C, et al. Intensive glycaemic control for patients with type 2 diabetes: systematic review with meta‐analysis and trial sequential analysis of randomised clinical trials. BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.) 2011;343:d6898. [PUBMED: 22115901] - PMC - PubMed
Hershon 2016
Higgins 2002
-
- Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta‐analysis. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21:1539‐58. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2009
Higgins 2011
Higgins 2011a
Higgins 2011b
-
- Higgins JP, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (editors). Chapter 16: Special topics in statistics. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.cochrane.org.
Higgins 2017
-
- Higgins JP, Altman DG, Sterne JA (editors). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Churchill R, Chandler J, Cumpston MS (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.2.0 (updated June 2017), Cochrane, 2017. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Hou 2015
-
- Hou L, Zhao T, Liu Y, Zhang Y. Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin compared with sulfonylurea therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes showing inadequately controlled glycosylated hemoglobin with metformin monotherapy: a meta‐analysis. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 2015;9(4):1528‐36. - PMC - PubMed
Hozo 2005
Hróbjartsson 2013
-
- Hróbjartsson A, Thomsen AS, Emanuelsson F, Tendal B, Hilden J, Boutron I, et al. Observer bias in randomized clinical trials with measurement scale outcomes: a systematic review of trials with both blinded and nonblinded assessors. Canadian Medical Association Journal 2013;185(4):E201‐11. - PMC - PubMed
ICH 1997
-
- International Conference on Harmonisation Expert Working Group. International conference on harmonisation of technical requirements for registration of pharmaceuticals for human use. ICH harmonised tripartite guideline. Guideline for good clinical practice //1997 CFR & ICH Guidelines. PA 19063‐2043. USA: Barnett International/PAREXEL, 1997.
Inzucchi 2012
-
- Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, Diamant M, Ferrannini E, Nauck M, et al. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: a patient‐centered approach: position statement of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care 2012;35(6):1364‐79. [PUBMED: 22517736] - PMC - PubMed
Johnson 2002
-
- Johnson JA, Majumdar SR, Simpson SH, Toth EL. Decreased mortality associated with the use of metformin compared with sulfonylurea monotherapy in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2002;25(12):2244‐8. [PUBMED: 12453968] - PubMed
Jones 2015
Kahler 2007
-
- Kahler KH, Rajan M, Rhoads GG, Safford MM, Demissie K, Lu SE, et al. Impact of oral antihyperglycemic therapy on all‐cause mortality among patients with diabetes in the Veterans Health Administration. Diabetes Care 2007;30(7):1689‐93. [PUBMED: 17440170] - PubMed
Kannan 2015
-
- Kannan S, Mahadevan S, Ramakrishnan A. Fixed dose combinations for type 2 diabetes. Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology 2015;3(6):408. - PubMed
Kirkham 2010
Krentz 2005
-
- Krentz AJ, Bailey CJ. Oral antidiabetic agents: current role in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Drugs 2005;65(3):385‐411. [PUBMED: 15669880] - PubMed
Kuecker 2016
Lan 1983
-
- Lan KK, DeMets DL. Discrete sequential boundaries for clinical trials. Biometrika 1983;70:659‐63.
Langtry 1998
-
- Langtry HD, Balfour JA. Glimepiride. A review of its use in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Drugs 1998;55(4):563‐84. [PUBMED: 9561345] - PubMed
LeRoith 2002
-
- LeRoith D. Beta‐cell dysfunction and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes: role of metabolic and genetic abnormalities. American Journal of Medicine 2002;113 Suppl 6A:3S‐11S. [PUBMED: 12431757] - PubMed
Liberati 2009
Lim 2015
Liu 2014
-
- Liu X, Xiao Q, Zhang L, Yang Q, Liu X, Xu L, et al. The long‐term efficacy and safety of DPP‐IV inhibitors monotherapy and in combination with metformin in 18,980 patients with type‐2 diabetes mellitus‐‐a meta‐analysis. Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety 2014;23(7):687‐98. - PubMed
Lundh 2017
Maruthur 2016
-
- Maruthur NM, Tseng E, Hutfless S, Wilson LM, Suarez‐Cuervo C, Berger Z, et al. Diabetes medications as monotherapy or metformin‐based combination therapy for type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Annals of Internal Medicine 2016;164(11):740‐51. [DOI: 10.7326/M15-2650] - DOI - PubMed
Mathieu 2009
-
- Mathieu S, Boutron I, Moher D, Altman DG, Ravaud P. Comparison of registered and published primary outcomes in randomized controlled trials. JAMA 2009;302:977‐84. - PubMed
McCall 2001
-
- McCall AL. Clinical review of glimepiride. Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy 2001;2(4):699‐713. [PUBMED: 11336617] - PubMed
Meader 2014
Mearns 2015
Megan 2012
-
- Megan B, Pickering RM, Weatherall M. Design, objectives, execution and reporting of published open‐label extension studies. Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice 2012;18(2):209‐15. - PubMed
Mishriky 2015
-
- Mishriky BM, Cummings DM, Tanenberg RJ. The efficacy and safety of DPP4 inhibitors compared to sulfonylureas as add‐on therapy to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice 2015;109(2):378‐88. - PubMed
Monami 2008
-
- Monami M, Lamanna C, Marchionni N, Mannucci E. Comparison of different drugs as add‐on treatments to metformin in type 2 diabetes: a meta‐analysis. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice 2008;79(2):196‐203. - PubMed
Morgan 2014
-
- Morgan CL, Mukherjee J, Jenkins‐Jones S, Holden SE, Currie CJ. Association between first‐line monotherapy with sulphonylurea versus metformin and risk of all‐cause mortality and cardiovascular events: a retrospective, observational study. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2014;16(10):957‐62. [PUBMED: 24720708] - PubMed
Nathan 2009
-
- Nathan DM, Buse JB, Davidson MB, Ferrannini E, Holman RR, Sherwin R, et al. Medical management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a consensus algorithm for the initiation and adjustment of therapy: a consensus statement from the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetologia 2009;52(1):17‐30. [PUBMED: 18941734] - PubMed
Nishio 2015
Odawara 2015
Pantalone 2012
-
- Pantalone KM, Kattan MW, Yu C, Wells BJ, Arrigain S, Jain A, et al. Increase in overall mortality risk in patients with type 2 diabetes receiving glipizide, glyburide or glimepiride monotherapy versus metformin: a retrospective analysis. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2012;14(9):803‐9. [PUBMED: 22486923] - PubMed
Phung 2010
-
- Phung OJ, Scholle JM, Talwar M, Coleman CI. Effect of noninsulin antidiabetic drugs added to metformin therapy on glycemic control, weight gain, and hypoglycemia in type 2 diabetes. JAMA 2010;303(14):1410‐8. - PubMed
Phung 2014
-
- Phung OJ, Sobieraj DM, Engel SS, Rajpathak SN. Early combination therapy for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: systematic review and meta‐analysis. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2014;16(5):410‐7. - PubMed
Pogue 1997
-
- Pogue JM, Yusuf S. Cumulating evidence from randomized trials: utilizing sequential monitoring boundaries for cumulative meta‐analysis. Controlled Clinical Trials 1997;18(6):580‐93; discussion 661‐6. [PUBMED: 9408720] - PubMed
Reid 2016
Review Manager 2014 [Computer program]
-
- Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager 5 (RevMan 5). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Riley 2011
-
- Riley RD, Higgins JP, Deeks JJ. Interpretation of random effects meta‐analyses. BMJ 2011;342:d549. - PubMed
Rosenstock 2013
-
- Rosenstock J, Marx N, Kahn SE, Zinman B, Kastelein JJ, Lachin JM, et al. Cardiovascular outcome trials in type 2 diabetes and the sulphonylurea controversy: rationale for the active‐comparator CAROLINA trial. Diabetes & Vascular Disease Research 2013;10(4):289‐301. - PubMed
Rosenstock 2015
Roumie 2012
Salpeter 2010
Scheen 2016
-
- Scheen AJ. Dulaglutide (Trulicity(R)), a new once‐weekly agonist of glucagon‐like peptide‐1 receptors for type 2 diabetes. Revue Medicale de Liege 2016;71(3):154‐60. - PubMed
Scherer 2007
Schramm 2011
-
- Schramm TK, Gislason GH, Vaag A, Rasmussen JN, Folke F, Hansen ML, et al. Mortality and cardiovascular risk associated with different insulin secretagogues compared with metformin in type 2 diabetes, with or without a previous myocardial infarction: a nationwide study. European Heart Journal 2011;32(15):1900‐8. [PUBMED: 21471135] - PubMed
Schroll 2015
Schünemann 2017
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Higgins JP, Vist GE, Glasziou P, Akl E, et al. on behalf of the Cochrane GRADEing Methods Group and the Cochrane Statistical Methods Group. Chapter 11: Completing ‘Summary of findings’ tables and grading the confidence in or quality of the evidence. In: Higgins JPT, Churchill R, Chandler J, Cumpston MS (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 5.2.0 (updated June 2017). Cochrane, 2017. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Scott 2012
-
- Scott LJ. Repaglinide: a review of its use in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Drugs 2012;72(2):249‐72. [PUBMED: 22268393] - PubMed
Seufert 2014
-
- Seufert J. Oral add‐on therapy to metformin in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a direct comparison between canagliflozin and glimepiride. Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift (1946) 2014;139 Suppl 2:S65‐9. - PubMed
Sharma 2017
Sterne 2011
-
- Sterne JA, Sutton AJ, Ioannidis JP, Terrin N, Jones DR, Lau J, et al. Recommendations for examining and interpreting funnel plot asymmetry in meta‐analyses of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 2011;343:d4002. - PubMed
Sterne 2017
-
- Sterne JA, Egger M, Moher D, Boutron I (editors). Chapter 10: Addressing reporting biases. In: Higgins JPT, Churchill R, Chandler J, Cumpston MS (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 5.2.0 (updated June 2017), Cochrane, 2017. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
UGDP 1976
-
- University Group Diabetes Program. A study of the effects of hypoglycemia agents on vascular complications in patients with adult‐onset diabetes. VI. Supplementary report on nonfatal events in patients treated with tolbutamide. Diabetes 1976;25(12):1129‐53. [PUBMED: 992232] - PubMed
UKPDS‐33 1998
-
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood‐glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet 1998;352(9131):837‐53. [PUBMED: 9742976] - PubMed
UKPDS‐34 1998
-
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Effect of intensive blood‐glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 34). Lancet 1998;352(9131):854‐65. [PUBMED: 9742977] - PubMed
Varvaki 2016
Vist 2008
-
- Vist GE, Bryant D, Somerville L, Birminghem T, Oxman AD. Outcomes of patients who participate in randomized controlled trials compared to similar patients receiving similar interventions who do not participate. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2008, Issue 2. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.MR000009.pub4] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Wang 2017
-
- Wang F, He Y, Zhang R, Zeng Q, Zhao X. Combination therapy of metformin plus dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitor versus metformin plus sulfonylurea and their association with a decreased risk of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 2017;96(36):e7638. - PMC - PubMed
Wetterslev 2008
-
- Wetterslev J, Thorlund K, Brok J, Gluud C. Trial sequential analysis may establish when firm evidence is reached in cumulative meta‐analysis. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2008;61(1):64‐75. [PUBMED: 18083463] - PubMed
Whalen 2015
-
- Whalen K, Miller S, Onge ES. The role of sodium‐glucose co‐transporter 2 inhibitors in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Clinical Therapeutics 2015;37(6):1150‐66. - PubMed
WHO 1998
-
- Alberti KM, Zimmet PZ. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part I: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabetic Medicine 1998;15(7):539‐53. - PubMed
WHO 2015
-
- World Health Organization. Diabetes. www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs312/en/ (accessed 29 February 2016).
Wild 2004
-
- Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care 2004;27(5):1047‐53. [PUBMED: 15111519] - PubMed
Wong 2006a
Wong 2006b
Wood 2008
Zhou 2015
-
- Zhou 2015. The benefits and risks of DPP4‐inhibitors vs sulfonylureas for patients with type 2 diabetes: accumulated evidence from randomised controlled trial. International Journal of Clinical Practice 2016;70(2):132‐41. - PubMed
Zintzaras 2014
-
- Zintzaras E, Miligkos M, Ziakas P, Balk EM, Mademtzoglou D, Doxani C, et al. Assessment of the relative effectiveness and tolerability of treatments of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a network meta‐analysis. Clinical Therapeutics 2014;36(10):1443‐53. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Madsen 2016
-
- Madsen KS, Kähler P, Kähler LK, Madsbad S, Metzendorf M‐I, Richter B, et al. Metformin and sulphonylurea (second‐ or third‐generation) combination therapy for adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2016, Issue 9. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012368] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

