Early neutropenia on day 8 treated with adjuvant Docetaxel-based chemotherapy in early breast cancer patients: Putative mechanisms within the neutrophil pool system
- PMID: 30998754
- PMCID: PMC6472781
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215576
Early neutropenia on day 8 treated with adjuvant Docetaxel-based chemotherapy in early breast cancer patients: Putative mechanisms within the neutrophil pool system
Abstract
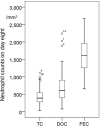
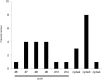
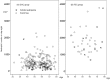
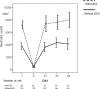
Most chemotherapy regimens cause neutropenic nadirs between days 10 and 14, and administration of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) support relies on this timing. In docetaxel (DOC)-based chemotherapy, the frequency of febrile neutropenia (FN) and the G-CSF dose administered varied greatly between studies. Our study goal was to forecast the necessary dose of G-CSF by comparing day 8 neutropenia with putative changes within the neutrophil pool. We conducted a retrospective observational analysis of 242 early breast cancer patients who had received adjuvant DOC-based chemotherapy (DOC group) compared with 43 patients who had received FEC chemotherapy (FEC group). Patients who were given a standard dose and had a blood test on day 8 in the 1st cycle were eligible. In the DOC group, patients routinely received prophylactic administration of G-CSF (150 μg/body) on day 3 and received additional G-CSF based on a blood test on day 8. Results of the day 8 blood test showed that severe neutropenia (<500/mm3, average 494/mm3) was observed in 152 out of 242 (62.8%) patients in the DOC group, while in the FEC group (n = 43), neutropenia was ambiguous (average 1,741/mm3). In the FEC group, 9 out of 43 patients (20.9%) and in the DOC group, 27 out of 242 patients (11.1%) experienced FN. In the DOC group, day 8 neutropenia was predictive for FN in a logistic regression model (OR 0.79 [95% CI: 0.655-0.952], p = 0.013). Among 214 patients under 70 years old, the planned chemotherapy cycle was completed in 190 (88.8%) patients who also received the maximum dose of G-CSF (150 μg/body) four times, while 23 patients could not complete the planned chemotherapy cycle, but only five because of FN-related complications. Patients treated with DOC should be treated for primary prophylaxis with G-CSF support at an earlier time starting with a relatively small dose.
Conflict of interest statement
The author has declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Incidence of febrile neutropenia in early stage breast cancer patients receiving adjuvant FEC-D treatment.Support Care Cancer. 2014 Dec;22(12):3227-34. doi: 10.1007/s00520-014-2318-9. Epub 2014 Jul 5. Support Care Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24996828
-
Impact of colony-stimulating factors to reduce febrile neutropenic events in breast cancer patients receiving docetaxel plus cyclophosphamide chemotherapy.Support Care Cancer. 2011 Apr;19(4):497-504. doi: 10.1007/s00520-010-0843-8. Epub 2010 Mar 17. Support Care Cancer. 2011. PMID: 20232087
-
The use of chemotherapy regimens carrying a moderate or high risk of febrile neutropenia and the corresponding management of febrile neutropenia: an expert survey in breast cancer and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.BMC Cancer. 2010 Nov 23;10:642. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-642. BMC Cancer. 2010. PMID: 21092320 Free PMC article.
-
2010 update of EORTC guidelines for the use of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor to reduce the incidence of chemotherapy-induced febrile neutropenia in adult patients with lymphoproliferative disorders and solid tumours.Eur J Cancer. 2011 Jan;47(1):8-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2010.10.013. Epub 2010 Nov 20. Eur J Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21095116
-
Colony-stimulating factors for the management of neutropenia in cancer patients.Drugs. 2002;62 Suppl 1:1-15. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200262001-00001. Drugs. 2002. PMID: 12479591 Review.
Cited by
-
Semimechanistic pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic model of tripegfilgrastim for pediatric patients after chemotherapy.CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2023 Sep;12(9):1319-1334. doi: 10.1002/psp4.13012. Epub 2023 Aug 9. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37559343 Free PMC article.
-
Parallel Toxicities: A Comparative Analysis of Chemotherapy-Induced Neutropenia and Alopecia.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Mar 30;17(7):1163. doi: 10.3390/cancers17071163. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40227705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The TH1902 Docetaxel Peptide-Drug Conjugate Inhibits Xenografts Growth of Human SORT1-Positive Ovarian and Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Stem-like Cells.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Sep 9;14(9):1910. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14091910. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36145658 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in Neutrophil Count During Valganciclovir Therapy for Symptomatic Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection.Biomedicines. 2025 Jul 16;13(7):1739. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13071739. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40722810 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) v5.0. Available from: https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocolDevelopment/electronic_applications/docs... - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

