KLF4 activates NFκB signaling and esophageal epithelial inflammation via the Rho-related GTP-binding protein RHOF
- PMID: 30998758
- PMCID: PMC6472825
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215746
KLF4 activates NFκB signaling and esophageal epithelial inflammation via the Rho-related GTP-binding protein RHOF
Abstract
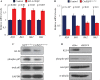
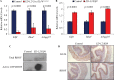
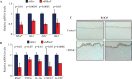
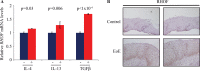
Understanding the regulatory mechanisms within esophageal epithelia is essential to gain insight into the pathogenesis of esophageal diseases, which are among the leading causes of morbidity and mortality throughout the world. The zinc-finger transcription factor Krüppel-like factor (KLF4) is implicated in a large number of cellular processes, such as proliferation, differentiation, and inflammation in esophageal epithelia. In murine esophageal epithelia, Klf4 overexpression causes chronic inflammation which is mediated by activation of NFκB signaling downstream of KLF4, and this esophageal inflammation produces epithelial hyperplasia and subsequent esophageal squamous cell cancer. Yet, while NFκB activation clearly promotes esophageal inflammation, the mechanisms by which NFκB signaling is activated in esophageal diseases are not well understood. Here, we demonstrate that the Rho-related GTP-binding protein RHOF is activated by KLF4 in esophageal keratinocytes, leading to the induction of NFκB signaling. Moreover, RHOF is required for NFκB activation by KLF4 in esophageal keratinocytes and is also important for esophageal keratinocyte proliferation and migration. Finally, we find that RHOF is upregulated in eosinophilic esophagitis, an important esophageal inflammatory disease in humans. Thus, RHOF activation of NFκB in esophageal keratinocytes provides a potentially important and clinically-relevant mechanism for esophageal inflammation and inflammation-mediated esophageal squamous cell cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Klf4 overexpression activates epithelial cytokines and inflammation-mediated esophageal squamous cell cancer in mice.Gastroenterology. 2010 Dec;139(6):2124-2134.e9. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.08.048. Gastroenterology. 2010. PMID: 20816834 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of Kruppel-like factor 5 in esophageal epithelia in vivo leads to increased proliferation in basal but not suprabasal cells.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007 Jun;292(6):G1784-92. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00541.2006. Epub 2007 Mar 29. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17395897
-
Klf4 Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation by Inducing Expression of MCP-1 Induced Protein 1 to Deubiquitinate TRAF6.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;47(6):2278-2290. doi: 10.1159/000491538. Epub 2018 Jul 5. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29975947
-
Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4): What we currently know.Gene. 2017 May 5;611:27-37. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.02.025. Epub 2017 Feb 22. Gene. 2017. PMID: 28237823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of KLF4 and inflammatory disease: Current status and future perspective.Pharmacol Res. 2024 Sep;207:107345. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107345. Epub 2024 Aug 10. Pharmacol Res. 2024. PMID: 39134187 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of an N6-methyladenosine-mediated positive feedback loop that promotes Epstein-Barr virus infection.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100547. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100547. Epub 2021 Mar 16. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33741341 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal multiomic modeling reveals a B-cell receptor proliferative program in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Leukemia. 2021 May;35(5):1463-1474. doi: 10.1038/s41375-021-01221-5. Epub 2021 Apr 8. Leukemia. 2021. PMID: 33833385 Free PMC article.
-
The Kruppel-like factor 4-signal transducer and activator of transcription 5A axis promotes pancreatic fibrosis in mice with caerulein-induced chronic pancreatitis.Exp Anim. 2023 Aug 7;72(3):379-388. doi: 10.1538/expanim.22-0147. Epub 2023 Mar 23. Exp Anim. 2023. PMID: 36948613 Free PMC article.
-
High Expression of RhoF Predicts Worse Overall Survival: A Potential Therapeutic Target for non-M3 Acute Myeloid Leukemia.J Cancer. 2021 Jul 25;12(18):5530-5542. doi: 10.7150/jca.52648. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34405015 Free PMC article.
-
Determining the immune environment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma lesions through the assessment of lesional blood drops.Sci Rep. 2021 Oct 4;11(1):19629. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-98804-0. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34608214 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

