Quality Evaluation of Gastrodia Elata Tubers Based on HPLC Fingerprint Analyses and Quantitative Analysis of Multi-Components by Single Marker
- PMID: 30999716
- PMCID: PMC6515102
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24081521
Quality Evaluation of Gastrodia Elata Tubers Based on HPLC Fingerprint Analyses and Quantitative Analysis of Multi-Components by Single Marker
Abstract
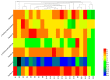
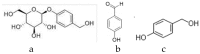
Gastrodia elata (G. elata) tuber is a valuable herbal medicine used to treat many diseases. The procedure of establishing a reasonable and feasible quality assessment method for G. elata tuber is important to ensure its clinical safety and efficacy. In this research, an effective and comprehensive evaluation method for assessing the quality of G. elata has been developed, based on the analysis of high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) fingerprint, combined with the quantitative analysis of multi-components by single marker (QAMS) method. The contents of the seven components, including gastrodin, p-hydroxybenzyl alcohol, p-hydroxy benzaldehyde, parishin A, parishin B, parishin C, and parishin E were determined, simultaneously, using gastrodin as the reference standard. The results demonstrated that there was no significant difference between the QAMS method and the traditional external standard method (ESM) (p > 0.05, RSD < 4.79%), suggesting that QAMS was a reliable and convenient method for the content determination of multiple components, especially when there is a shortage of reference substances. In conclusion, this strategy could be beneficial for simplifying the processes in the quality control of G. elata tuber and giving references to promote the quality standards of herbal medicines.
Keywords: Gastrodia elata tuber; HPLC; QAMS; quality evaluation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Li Z.F., Wang Y.W., Ouyang H., Lu Y., Qiu Y., Feng Y.L., Jiang H.L., Zhou X., Yang S.L. A novel dereplication strategy for the identification of two new trace compounds in the extract of Gastrodia elata using UHPLC/Q-TOF-MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. B. 2015;988:45–52. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2015.02.020. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hu M., Yan H., Fu Y., Jiang Y., Yao W., Yu S., Zhang L., Wu Q., Ding A., Shan M. Optimal extraction study of gastrodin-type components from Gastrodia Elata tubers by response surface design with integrated phytochemical and bioactivity evaluation. Molecules. 2019;24:547. doi: 10.3390/molecules24030547. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

