Impact of polyols on Oral microbiome of Estonian schoolchildren
- PMID: 30999906
- PMCID: PMC6471963
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-019-0747-z
Impact of polyols on Oral microbiome of Estonian schoolchildren
Abstract
Background: Oral microbiome has significant impact on both oral and general health. Polyols have been promoted as sugar substitutes in prevention of oral diseases. We aimed to reveal the effect of candies containing erythritol, xylitol or control (sorbitol) on salivary microbiome.
Methods: Ninety children (11.3 ± 0.6 years) consumed candies during 3 years. Microbial communities were profiled using Illumina HiSeq 2000 sequencing and real-time PCR.
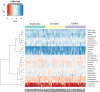
Results: The dominant phyla in saliva were Firmicutes (39.1%), Proteobacteria (26.1%), Bacteroidetes (14.7%), Actinobacteria (12%) and Fusobacteria (6%). The microbiome of erythritol group significantly differed from that of the other groups. Both erythritol and xylitol reduced the number of observed bacterial phylotypes in comparison to the control group. The relative abundance of the genera Veillonella, Streptococcus and Fusobacterium were higher while that of Bergeyella lower after erythritol intervention when comparing with control. The lowest prevalence of caries-related mutans streptococci corresponded with the lowest clinical caries markers in the erythritol group.
Conclusions: Daily consumption of erythritol, xylitol or control candies has a specific influence on the salivary microbiome composition in schoolchildren. Erythritol is associated with the lowest prevalence of caries-related mutans streptococci and the lowest levels of clinical caries experience.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier NCT01062633.
Keywords: Erythritol; Next generation sequencing; Oral microbiome; Polyol; Saliva; qPCR.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was performed according to Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Review Committee on Human Research of the University of Tartu (no. 166/7 17.12.2007). The written agreement forms were signed by parents or caretakers of the participants.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
Joan Vermeiren, Douwina Bosscher and Peter de Cock were employed by Cargill during the preparation of this manuscript, and Cargill produces erythritol. No potential conflict of interest was reported by other authors.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

