Circular RNA hsa_circ_0068871 regulates FGFR3 expression and activates STAT3 by targeting miR-181a-5p to promote bladder cancer progression
- PMID: 30999937
- PMCID: PMC6472097
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-019-1136-9
Circular RNA hsa_circ_0068871 regulates FGFR3 expression and activates STAT3 by targeting miR-181a-5p to promote bladder cancer progression
Abstract
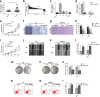
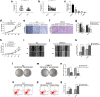
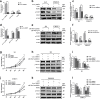
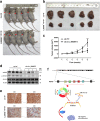
Background: FGFR3 plays an important role in the development of bladder cancer (BCa). Hsa_circ_0068871 is a circRNA generated from several exons of FGFR3. However, the potential functional role of hsa_circ_0068871 in BCa remains largely unknown. Here we aim to evaluate the role of hsa_circ_0068871 in BCa.
Methods: We selected miR-181a-5p as the potential target miRNA of hsa_circ_0068871. The expression levels of hsa_circ_0068871 and miR-181a-5p were examined in BCa tissues and paired adjacent normal tissues by quantitative real-time PCR. To characterize the function of hsa_circ_0068871, BCa cell lines were stably infected with lentivirus targeting hsa_circ_0068871, followed by examinations of cell proliferation, migration and apoptosis. In addition, xenografts experiment in nude mice were performed to evaluate the effect of hsa_circ_0068871 in BCa. Biotinylated RNA probe pull-down assay, fluorescence in situ hybridization and luciferase reporter assay were conducted to confirm the relationship between hsa_circ_0068871, miR-181a-5p and FGFR3.
Results: Hsa_circ_0068871 is over-expressed in BCa tissues and cell lines, whereas miR-181a-5p expression is repressed. Depletion of has_circ_0068871 or upregulation of miR-181a-5p inhibited the proliferation and migration of BCa cells in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, hsa_circ_0068871 upregulated FGFR3 expression and activated STAT3 by targeting miR-181a-5p to promote BCa progression.
Conclusions: Hsa_circ_0068871 regulates the miR-181a-5p/FGFR3 axis and activates STAT3 to promote BCa progression, and it may serve as a potential biomarker.
Keywords: Bladder cancer; FGFR3; STAT3; hsa_circ_0068871; miR-181a-5p.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval
Animal experiments were conducted in mice using protocols approved by the Ethics Committee of Shanghai Tenth People’s Hospital of Tongji University, and written informed consent was obtained from all patients or their relatives.
Consent for publication
We have obtained consents to publish this paper from all the participants of this study.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

