A potential function of RLIP76 in the ovarian corpus luteum
- PMID: 30999946
- PMCID: PMC6474048
- DOI: 10.1186/s13048-019-0510-8
A potential function of RLIP76 in the ovarian corpus luteum
Abstract
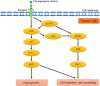
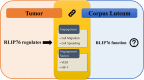
Ral interacting protein of 76 kDa (RLIP76) is multifunctional protein localized and distributed in the plasma membrane, cytosol, and nucleus of the cell. In tumorigenesis, RLIP76 emerges as a common feature for the solid tumor growth. RLIP76 is ubiquitously expressed in various tissues including the ovary. Interestingly, the similar physiological events in obtaining an adequate supply of nutrient by gaining access to the host vascular system are required either for corpus luteum formation or tumor development. In addition, the identical angiogenesis modulators were found in neoplastic and normal ovaries. Our previous study involving RLIP76-/- mice implanted with melanoma or carcinoma cell conclusively demonstrated that RLIP76 is necessary for angiogenesis and neovascularization of primary solid tumors. RLIP76 plays an essential role in tumor angiogenesis through the regulation of pro-angiogenic factors such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1). In certain previous studies, those pro-angiogenic factors were found significantly to be upregulated during the corpus luteum formation. To that, the following review will discuss the likelihood of RLIP76 role in ovarian corpus luteum.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Corpus luteum; Ovary; RLIP76.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The potential role of Ral-interacting protein 76 and vascular endothelial growth factor on angiogenesis in the tumor and ovarian corpus luteum microenvironment.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Oct 31;13(10):5702-5710. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-770. Epub 2024 Oct 17. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39525031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crucial Role of RLIP76 in Promoting Glycolysis and Tumorigenesis by Stabilization of HIF-1α in Glioma Cells Under Hypoxia.Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Nov;59(11):6724-6739. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02999-w. Epub 2022 Aug 23. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35998001
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor inhibition affects luteal function with no effect on fertility in mice.Reproduction. 2025 Jan 21;169(2):e240313. doi: 10.1530/REP-24-0313. Print 2024 Feb 1. Reproduction. 2025. PMID: 39652635
-
The non-ABC drug transporter RLIP76 (RALBP-1) plays a major role in the mechanisms of drug resistance.Curr Drug Metab. 2007 May;8(4):315-23. doi: 10.2174/138920007780655414. Curr Drug Metab. 2007. PMID: 17504221 Review.
-
RLIP76 regulates HIF-1 activity, VEGF expression and secretion in tumor cells, and secretome transactivation of endothelial cells.FASEB J. 2014 Sep;28(9):4158-68. doi: 10.1096/fj.14-255711. Epub 2014 Jun 13. FASEB J. 2014. PMID: 24928198 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Functional role of circadian clock system in steroidogenesis and cell death pathways during corpus luteum regression in cattle.Cell Tissue Res. 2025 Jul 24. doi: 10.1007/s00441-025-03997-9. Online ahead of print. Cell Tissue Res. 2025. PMID: 40702377
-
Progestin and adipoQ receptor 7 (PAQR7) mediate the anti-apoptotic effect of P4 on human granulosa cells and its deficiency reduces ovarian function in female mice.J Ovarian Res. 2024 Feb 6;17(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s13048-024-01348-w. J Ovarian Res. 2024. PMID: 38317224 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic changes in mitochondrial 3D structure during folliculogenesis and luteal formation in the goat large luteal cell lineage.Sci Rep. 2021 Jul 30;11(1):15564. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-95161-w. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34330986 Free PMC article.
-
Haploinsufficiency Interactions of RALBP1 and TP53 in Carcinogenesis.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jan 12;13(2):255. doi: 10.3390/cancers13020255. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33445456 Free PMC article.
-
The potential role of Ral-interacting protein 76 and vascular endothelial growth factor on angiogenesis in the tumor and ovarian corpus luteum microenvironment.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Oct 31;13(10):5702-5710. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-770. Epub 2024 Oct 17. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39525031 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tomac J, Cekinovć D, Arapović J. Biology of the corpus luteum. Period Biol. 2011;1131:43–49.
-
- Devoto L, Fuentes A, Kohen P, Cespedes P, Palomino A, Pommer R, et al. The human corpus luteum: life cycle and function in natural cycles. Reprod Endocrinol. 2009;923:1067–1079. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

