Epidemiology of confirmed coronary heart disease among population older than 60 years in rural central India-A community-based cross-sectional study
- PMID: 31000181
- PMCID: PMC6477189
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ihj.2019.01.002
Epidemiology of confirmed coronary heart disease among population older than 60 years in rural central India-A community-based cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: Three-fifths of total deaths in India are attributed to noncommunicable diseases, and coronary heart disease (CHD) is one of the dominant causes. There are only few studies available in India to find confirmed CHD by pragmatic approach. This study aims to find prevalence of confirmed CHD and its risk factors in rural community of central India.
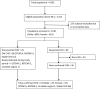
Materials and methods: This was a community-based cross-sectional study during 2013-2014 involving adults ≥60 years from 13 villages in rural central India. We screened CHD on the basis of history and standard 12-lead ECG. Apart from the past documentation of CHD, we diagnosed confirmed CHD in symptomatic patients or with resting ECG changes by means of echocardiography, exercise ECG test or coronary angiography whenever needed.
Results: We screened 1190 of 1415 individuals ≥60 years for CHD. Five hundred eighty were men and 610 were women. Diagnosis of CHD was confirmed in 61 individuals (29 men and 32 women). The prevalence of CHD in individuals older than 60 years was 51.3 per 1000 population. Hypertension was the only independent risk factor associated with CHD, whereas association of diabetes mellitus, obesity, socioeconomic status and smoking with CHD was not significant.
Conclusion: Prevalence of confirmed CHD has increased in agrarian rural community in central India, which requires further studies to find out causative factors.
Keywords: Coronary heart disease; Epidemiology; Rural India.
Copyright © 2019 Cardiological Society of India. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . vol. 3. 2015. Global Health Observatory (GHO) Data 2015; p. 23. Retrieved.
-
- Report on Medical Certification of Cause of Death. Office of the Registrar General of India, Government of India; 2015. http://www.censusindia.gov.in/2011-Documents/mccd_Report1/MCCD_Report-20... [Internet] Ministry of Home Affairs, Vital Statistics Division R. K. Puram New Delhi [cited 01/03/2018]. Available from:
-
- Goyal A., Yusuf S. The burden of cardiovascular disease in the Indian subcontinent. Indian J Med Res. 2006;124(3):235–244. - PubMed
-
- Srinath Reddy K., Shah B., Varghese C., Ramadoss A. Responding to the threat of chronic diseases in India. Lancet. 2005;366(9498):1744–1749. - PubMed
-
- Organization W.H. vol. 9. WHO; Geneva: 2014. (Global Health Estimates: Deaths by Cause, Age, Sex and Country, 2000-2012).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous