Roles, Actions, and Therapeutic Potential of Specialized Pro-resolving Lipid Mediators for the Treatment of Inflammation in Cystic Fibrosis
- PMID: 31001110
- PMCID: PMC6454233
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00252
Roles, Actions, and Therapeutic Potential of Specialized Pro-resolving Lipid Mediators for the Treatment of Inflammation in Cystic Fibrosis
Abstract
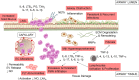
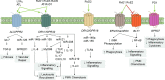
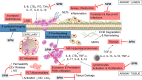
Non-resolving inflammation is the main mechanism of morbidity and mortality among patients suffering from cystic fibrosis (CF), the most common life-threatening human genetic disease. Resolution of inflammation is an active process timely controlled by endogenous specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators (SPMs) produced locally in inflammatory loci to restrain this innate response, prevent further damages to the host, and permit return to homeostasis. Lipoxins, resolvins, protectins, and maresins are SPM derived from polyunsaturated fatty acids that limit excessive leukocyte infiltration and pro-inflammatory signals, stimulate innate microbial killing, and enhance resolution. Their unique chemical structures, receptors, and bioactions are being elucidated. Accruing data indicate that SPMs carry protective functions against unrelenting inflammation and infections in preclinical models and human CF systems. Here, we reviewed their roles and actions in controlling resolution of inflammation, evidence for their impairment in CF, and proofs of principle for their exploitation as innovative, non-immunosuppressive drugs to address inflammation and infections in CF.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; chronic infections; homeostasis; lipid mediator; lung inflammation and fibrosis; macrophages; pharmacology; resolution.
Figures


Similar articles
-
E-series resolvin metabolome, biosynthesis and critical role of stereochemistry of specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs) in inflammation-resolution: Preparing SPMs for long COVID-19, human clinical trials, and targeted precision nutrition.Semin Immunol. 2022 Jan;59:101597. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2022.101597. Epub 2022 Feb 16. Semin Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35227568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators: a key player in resolving inflammation in autoimmune diseases.Sci Bull (Beijing). 2025 Mar 15;70(5):778-794. doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2024.07.049. Epub 2025 Jan 2. Sci Bull (Beijing). 2025. PMID: 39837719 Review.
-
Pro-Resolving Lipid Mediators (SPMs) and Their Actions in Regulating miRNA in Novel Resolution Circuits in Inflammation.Front Immunol. 2012 Oct 22;3:298. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00298. eCollection 2012. Front Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23093949 Free PMC article.
-
Pro-resolving lipid mediator Resolvin D1 serves as a marker of lung disease in cystic fibrosis.PLoS One. 2017 Feb 3;12(2):e0171249. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171249. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28158236 Free PMC article.
-
Novel mediators and mechanisms in the resolution of infectious inflammation: evidence for vagus regulation.J Intern Med. 2019 Sep;286(3):240-258. doi: 10.1111/joim.12871. Epub 2019 Jan 18. J Intern Med. 2019. PMID: 30565762 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of early treatment with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) on the bronchoalveolar lavage proteome and oxylipids during bovine respiratory syncytial virus (BRSV) infection.PLoS One. 2024 Nov 15;19(11):e0309609. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0309609. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39546485 Free PMC article.
-
Specialized Pro-Resolving Lipid Mediators in Pulmonary Diseases: Molecular and Therapeutic Implications.Molecules. 2025 May 19;30(10):2212. doi: 10.3390/molecules30102212. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40430385 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of Specialized Pro-Resolving Lipid Mediators in Autophagy and Inflammation.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 10;21(18):6637. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186637. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32927853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Could Arachidonic Acid-Derived Pro-Resolving Mediators Be a New Therapeutic Strategy for Asthma Therapy?Front Immunol. 2020 Dec 9;11:580598. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.580598. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33362766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the Heme Oxygenase 1/Carbon Monoxide Pathway to Resolve Lung Hyper-Inflammation and Restore a Regulated Immune Response in Cystic Fibrosis.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Jul 14;11:1059. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01059. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32760278 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdelmoaty S., Wigerblad G., Bas D. B., Codeluppi S., Fernandez-Zafra T., El-Awady el S., et al. (2013). Spinal actions of lipoxin A4 and 17(R)-resolvin D1 attenuate inflammation-induced mechanical hypersensitivity and spinal TNF release. PLoS One 8:e75543. 10.1371/journal.pone.0075543 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

