Pain, Parental Involvement, and Oxytocin in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
- PMID: 31001173
- PMCID: PMC6454868
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00715
Pain, Parental Involvement, and Oxytocin in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
Abstract
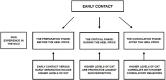
Preterm infants (PTI) typically experience many painful and stressful procedures or events during their first weeks of life in a neonatal intensive care unit, and these can profoundly impact subsequent brain development and function. Several protective interventions during this sensitive period stimulate the oxytocin system, reduce pain and stress, and improve brain development. This review provides an overview of the environmental risk factors experienced by PTI during hospitalization, with a focus on the effects of pain, and early maternal separation. We also describe the long-term adverse effects of the simultaneous experiences of pain and maternal separation, and the potential beneficial effects of maternal vocalizations, parental contact, and several related processes, which appear to be mediated by the oxytocin system.
Keywords: early contact; early separation; pain; parents; prematurity.
Figures
References
-
- Amini-Khoei H., Mohammadi-Asl A., Amiri S., Hosseini M. J., Momeny M., Hassanipour M., et al. (2017). Oxytocin mitigated the depressive-like behaviors of maternal separation stress through modulating mitochondrial function and neuroinflammation. Prog. Neuro Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 76 169–178. 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2017.02.022 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources