Biomarkers in Motor Neuron Disease: A State of the Art Review
- PMID: 31001186
- PMCID: PMC6456669
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00291
Biomarkers in Motor Neuron Disease: A State of the Art Review
Abstract
Motor neuron disease can be viewed as an umbrella term describing a heterogeneous group of conditions, all of which are relentlessly progressive and ultimately fatal. The average life expectancy is 2 years, but with a broad range of months to decades. Biomarker research deepens disease understanding through exploration of pathophysiological mechanisms which, in turn, highlights targets for novel therapies. It also allows differentiation of the disease population into sub-groups, which serves two general purposes: (a) provides clinicians with information to better guide their patients in terms of disease progression, and (b) guides clinical trial design so that an intervention may be shown to be effective if population variation is controlled for. Biomarkers also have the potential to provide monitoring during clinical trials to ensure target engagement. This review highlights biomarkers that have emerged from the fields of systemic measurements including biochemistry (blood, cerebrospinal fluid, and urine analysis); imaging and electrophysiology, and gives examples of how a combinatorial approach may yield the best results. We emphasize the importance of systematic sample collection and analysis, and the need to correlate biomarker findings with detailed phenotype and genotype data.
Keywords: ALS (Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis); biofluid; biomarker; cerebrospinal fluid (CSF); electrophysiology; motor neuron disease (MND); neuroimaging.
Figures

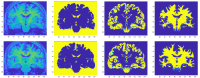
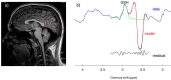
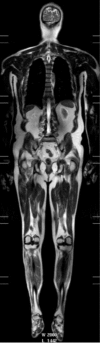
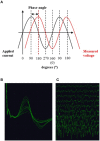
References
-
- Mitchell JD, Callagher P, Gardham J, Mitchell C, Dixon M, Addison-Jones R, et al. Timelines in the diagnostic evaluation of people with suspected amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)/motor neuron disease (MND)–a 20-year review: can we do better? Amyotroph Lateral Scler. (2010) 11:537–41. 10.3109/17482968.2010.495158 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

