Immediate Neutrophil-Variable-T Cell Receptor Host Response in Bacterial Meningitis
- PMID: 31001192
- PMCID: PMC6454057
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00307
Immediate Neutrophil-Variable-T Cell Receptor Host Response in Bacterial Meningitis
Abstract
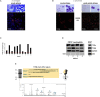
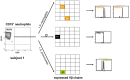
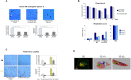
Bacterial meningitis is a life-threatening disease that evokes an intense neutrophil-dominated host response to microbes invading the subarachnoid space. Recent evidence indicates the existence of combinatorial V(D)J immune receptors in neutrophils that are based on the T cell receptor (TCR). Here, we investigated expression of the novel neutrophil TCRαβ-based V(D)J receptors in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from human patients with acute-phase bacterial meningitis using immunocytochemical, genetic immunoprofiling, cell biological, and mass spectrometric techniques. We find that the human neutrophil combinatorial V(D)J receptors are rapidly induced in CSF neutrophils during the first hours of bacterial meningitis. Immune receptor repertoire diversity is consistently increased in CSF neutrophils relative to circulating neutrophils and phagocytosis of baits directed to the variable immunoreceptor is enhanced in CSF neutrophils during acute-phase meningitis. Our results reveal that a flexible immune response involving neutrophil V(D)J receptors which enhance phagocytosis is immediately initiated at the site of acute bacterial infection.
Keywords: T cell receptors; V(D)J receptors; bacterial meningitis; neutrophil granulocytes; phagocytosis.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

